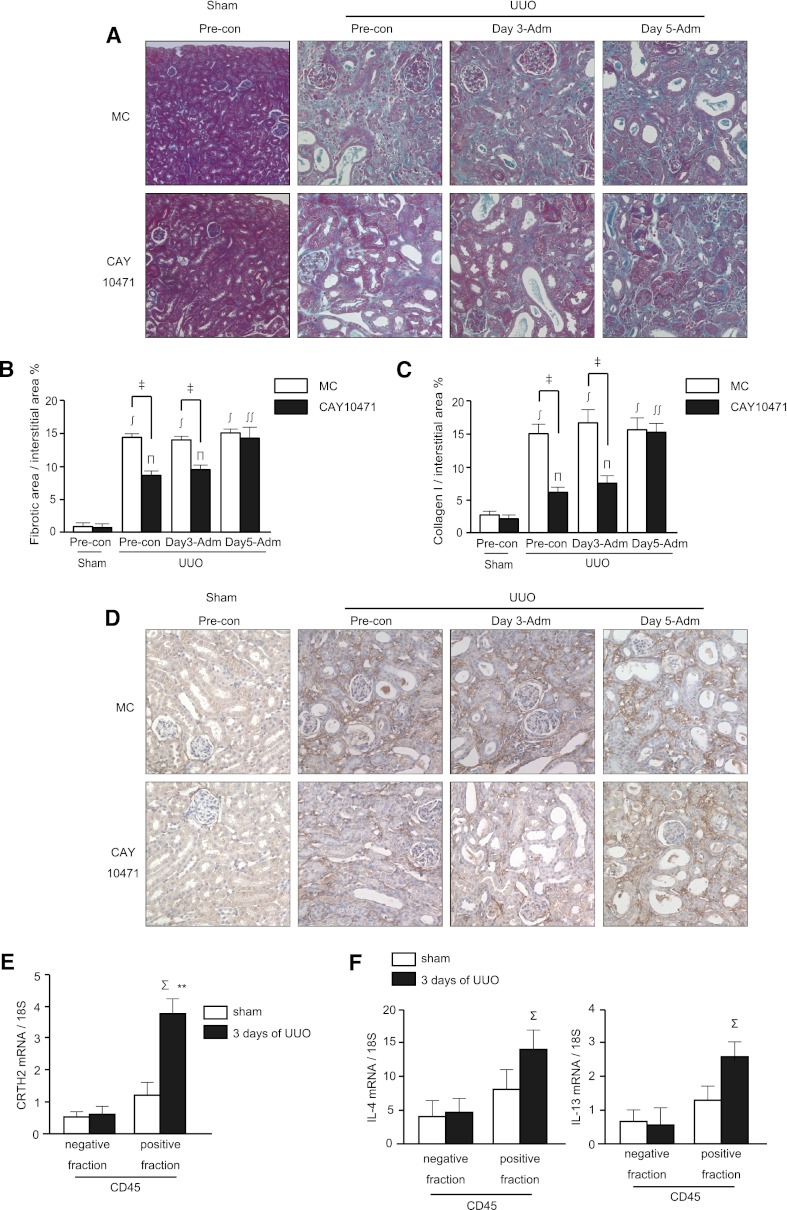
Figure 5.
Oral administration of CRTH2 antagonist, CAY10471, attenuated the progression of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. (A) Representative images of Azan staining. The number of mice in the sham, preconditioning (CAY-10471 administration was started at 4 days before UUO), and day 3 administration and day 5 administration (CAY-10471 administration was started at 3 or 5 days after UUO, respectively) groups was 3, 6, 5, and 5, respectively. (B) Quantitative assessment of the fibrotic area. Data are the mean ± SD. ‡P<0.05 versus MC-fed; ∫P<0.001 versus sham of MC-fed; πP<0.01 versus sham of CAY10471; ∫∫P<0.05 versus UUO with preconditioning and day 3 administration of CAY10471 (two-sided t test, respectively). (C) Quantitative assessment of the collagen I-positive area. Data are the mean ± SD. ‡P<0.05 versus MC-fed; ∫P<0.001 versus sham of MC-fed; πP<0.01 versus sham of CAY10471; ∫∫P<0.05 versus UUO with preconditioning and day 3 administration of CAY10471 (two-sided t test, respectively). (D) Collagen I staining of paraffin sections. Representative images are shown. (E and F) Either the CRTH2 mRNA (E) or IL-4/IL-13 mRNA (F) expression was significantly increased at 3 days after UUO in CD45-positive fractions, but not in CD45-negative fractions (n=4 for each assay, ΣP<0.05 versus negative fraction).