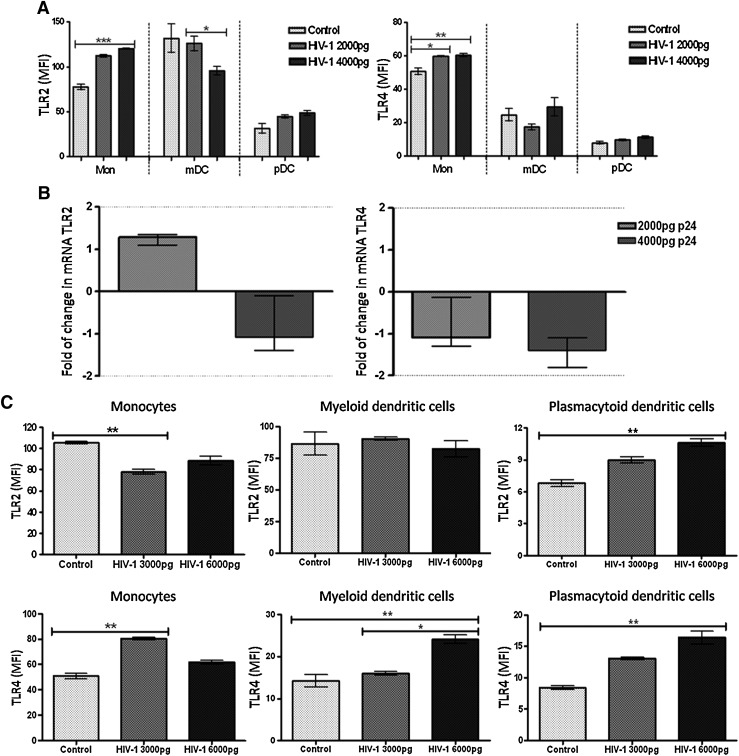
FIG. 1.
Modulation of TLR2 and TLR4 expression in monocytes and in dendritic cells (DCs) exposed to HIV-1 in vitro. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (1×106) were exposed in vitro to HIV-1H9 HTLV-IIIcc (2000 and 4000 pg p24 HIV-1) for 2 h, and then incubated for 18 h at 37°C and 5% CO2 (A and B), or exposed in vitro to HIV-1H9 HTLV-IIIcc (3000 and 6000 pg p24 HIV-1) for 2 h, and then incubated 1 h at 37°C and 5% CO2 (C). TLR2 and TLR4 expression was measured at the protein level by flow cytometry (A and C) and at the mRNA level by real time RT-PCR (B). For flow cytometry analyses, mononuclear cells were gated according to physical characteristics, excluding dead cells. Monocytes were then gated as CD14+ cells, myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) as Lin 1– CD11chigh, and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) as Lin 1– CD123high. Each specific subpopulation was plotted as a histogram to show the expression of TLR2 and TLR4 by flow cytometry. The data are presented as overall mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for toll-like receptors (TLRs) in each cell subpopulation, after subtraction of isotype staining background. Representative results of three independent experiments are shown as median and range. In the real time RT-PCR results, the dotted line represents 2-fold induction, compared to the control. Comparisons were performed using the Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA tests and Dunn's posttests. The level of significance was *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.