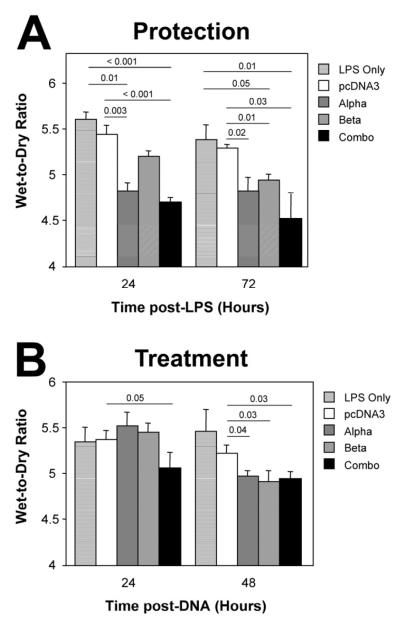
Figure 3. Electroporation-mediated gene transfer of subunits of the Na+,K+-ATPase can both protect from subsequent LPS-induced lung injury and reverse pre-existing LPS-induced lung injury.
A. Protection Studies. One hundred μg of plasmid in 50 μl were administered intratracheally to mice by electroporation. One day later, LPS (4 mg/kg) was administered to the lungs and 24 or 27 hours after this, lungs were removed for wet-to-dry ratio analysis (mean ± sem; n=5). B. Treatment Studies. LPS (4 mg/kg) was administered intratracheally to Balb/c mice and one day later, 100 μg of plasmid was delivered to the lungs by electroporation. Twenty-four or forty-eight hours later, lungs were removed for gravimetric analysis. Wet-to-dry ratios are shown as mean ± SEM (n=5). Statistical analysis was by non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. Taken with permission from ref ,51.