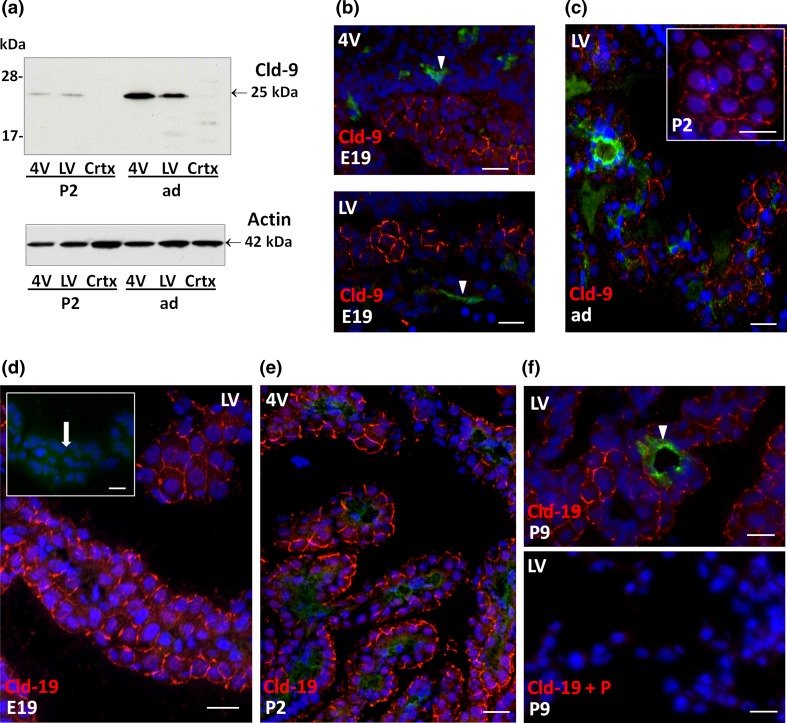
Fig. 5.
Detection of claudin-9 and claudin-19 in choroid plexus during rat brain development. a Representative Western blot of LVCP, 4VCP and cortex dissected from P2, and adult animals (10 μg per lane). Cld-9 protein was enriched in both 4V and LV compared to the cortex, and was higher in adult as compared to P2 animals (upper panel band at 25 kDa). Actin used as a loading indicator is shown in the lower panel (42 kDa band). b, c Cld-9 immunoreactivity (red) in the developing and adult brain. A distinct signal was associated with the CP epithelial cell membrane in selected areas of both LVCP and 4VCP in E19 animals (b). The staining was present at all intercellular junctions in P2 animals (insert c), and was observed throughout the CPs in adult animals (c). It was not associated with parenchymal vessels (arrowheads). d–f Cld-19 immunoreactivity (red) in the developing and adult brain. Choroid plexus epithelial cell membranes were distinctly labeled in E19 animals (d), displaying a typical honeycomb pattern. The insert shows a negative control obtained by omitting the primary antibody. The arrow localizes the CP. A strong signal was also observed in the epithelium at later stages, as illustrated for 4VCP in P2 (e) and LVCP in P9 (f upper panel) animals. No choroidal staining was observed when the Ab was preincubated with excess of immunogen peptide (P) (f lower panel). The signal was absent from the choroidal vessels (arrowhead f). In b, c, f, double immunolabeling with anti-RECA-1 Ab allowed visualizing the choroidal vessels. DAPI was used to stain nuclei. Scale bars 20 μm. Crtx cerebral cortex. Other abbreviations as in Fig. 2