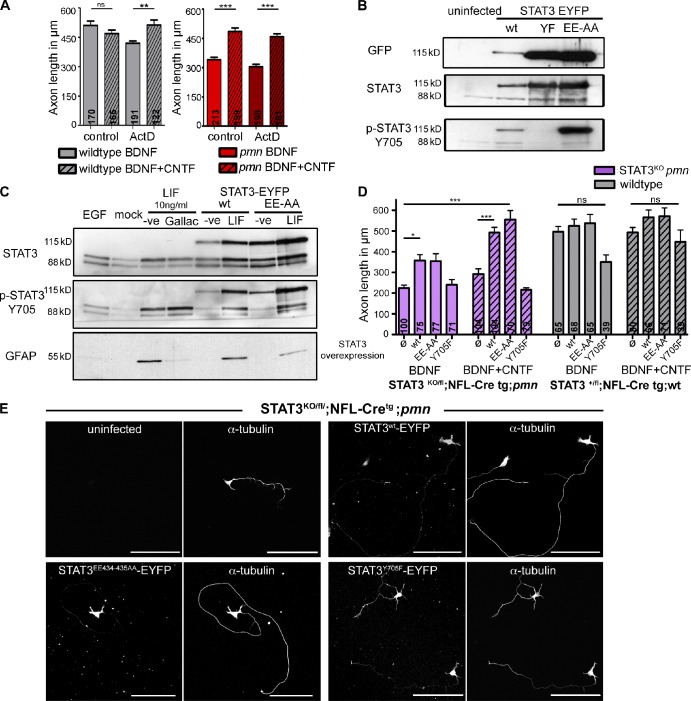
Figure 3.
Transcription-independent activity of STAT3 mediates axon growth in pmn mutant motoneurons. (A) Axon length of wild-type and pmn mutant motoneurons in control or 5 nM actinomycin D–treated cultures after 5 DIV. Actinomycin D (ActD) was applied at 4 DIV for 24 h. Numbers in bars indicate numbers of cells analyzed. n = 3 independent experiments. Statistical analysis: **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ANOVA with Bonferroni posthoc test. (B) Lentiviral overexpression of STAT3wt-EYFP, STAT3EE434–435AA-EYFP, and STAT3Y705F-EYFP in primary motoneurons. Wild-type and EE434–435AA mutant STAT3 can be activated at tyrosine 705 but not the STAT3Y705F-EYFP mutant. (C) LIF-induced GFAP induction in neural stem cells was reduced by STAT3EE434–435AA-EYFP and 10 µM galiellalactone (Gallac), indicating that mutant STAT3EE434–435AA-EYFP represses transcription of its target genes. (D) STAT3 phosphorylation, but not its transcriptional activity, is required for CNTF-mediated axon growth in pmn mutant motoneurons. Overexpression of STAT3EE434–435AA-EYFP mutant in STAT3-KO;pmn mutant motoneurons completely rescues axon growth upon CNTF application in contrast to STAT3Y705F-EYFP mutant. Ø represents uninfected, and WT, EE-AA, and Y705F represent lentiviral overexpression of STAT3WT-EYFP, STAT3EE434–435AA-EYFP, and STAT3Y705F-EYFP, respectively. Numbers in bars indicate numbers of cells analyzed. n = 3 independent experiments. Statistical analysis: *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ANOVA with Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. (E) Representative images of STAT3-KO;pmn mutant motoneurons overexpressing STAT3wt-EYFP, STAT3EE434–435AA-EYFP, and STAT3Y705F-EYFP and cultured with BDNF and CNTF. Bars, 100 µm. −ve, negative; wt, wild type. Data shown represent means ± SEM.