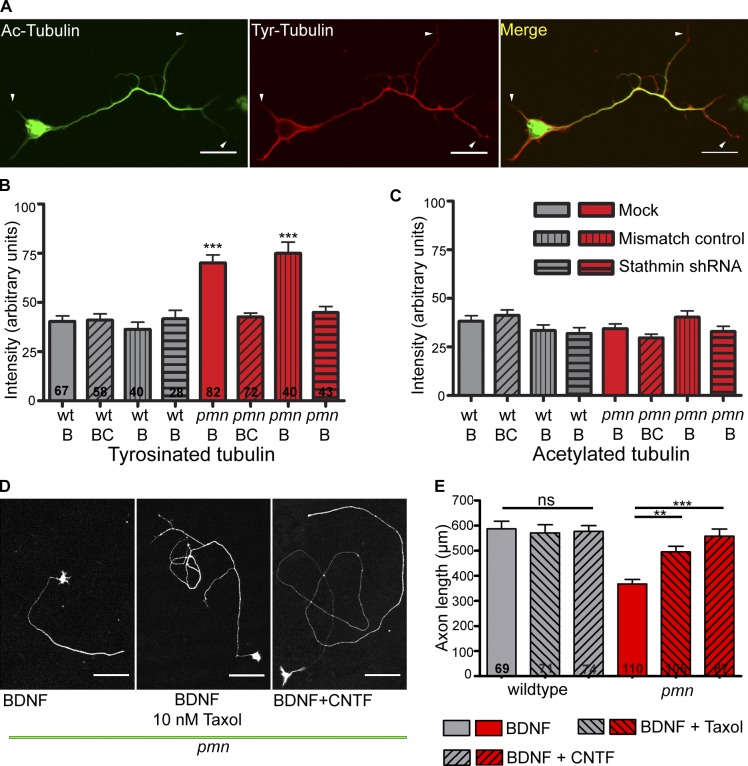
Figure 5.
MT stability is altered in pmn mutant motoneurons. (A) Wild-type motoneuron stained with antibodies against acetylated and tyrosinated α-tubulin. Acetylated (Ac) tubulin (Cy2) labels stabilized MTs and is enriched in the axons but relatively excluded from dendrites and axonal growth cones (arrowheads). Tyrosinated (Tyr) tubulin (Cy3) labels dynamic and unstable MTs, including those in dendrites and axonal tips as shown by arrowheads. Bars, 20 µm. (B and C) Levels of tyrosinated and acetylated tubulin in pmn mutant motoneurons. (B) Levels of tyrosinated tubulin were increased in pmn mutant motoneurons when compared with wild-type motoneurons. 10 ng/ml CNTF treatment or stathmin knockdown in pmn mutant motoneurons reduced tyrosinated tubulin levels to wild-type levels. (C) Levels of acetylated tubulin were unchanged under conditions investigated. Numbers in bars indicate number of cells analyzed. BDNF and CNTF are indicated by B and C, respectively. Statistical analysis: ***, P < 0.001; ANOVA with Bonferroni posthoc test. (D) Representative pictures of pmn mutant motoneurons cultured with BDNF, 10 nM taxol, and BDNF and CNTF showing increased axon length upon stabilization of MTs. Bars, 100 µm. (E) Stabilization of MTs in pmn mutant motoneurons in the presence of 10 nM taxol increased axon length in pmn motoneurons to wild-type levels. Numbers in bars represent cells measured. Statistical analysis: ***, P < 0.001; ANOVA with Bonferroni posthoc test. wt, wild type. Error bars shown represent means ± SEM from three independent experiments.