Abstract
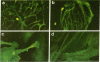
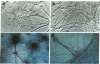
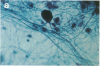
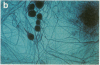
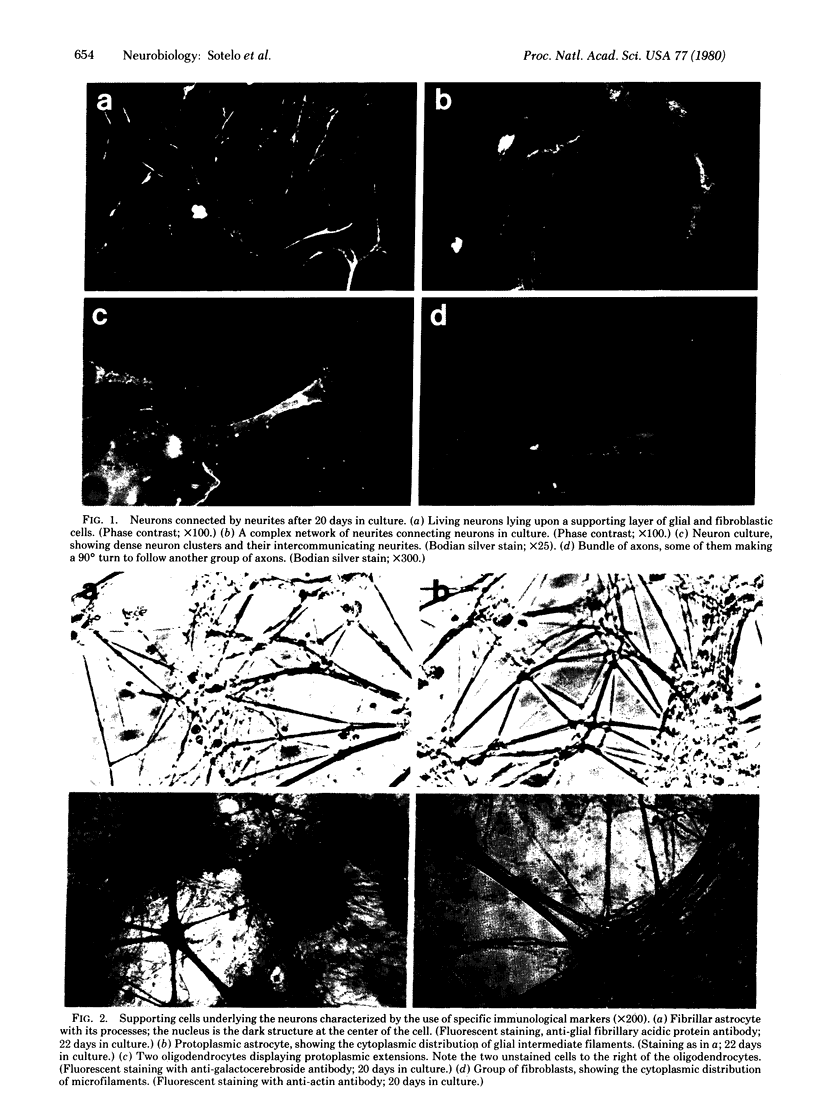
We report a simplified method for culturing fetal central nervous system cells predominantly inducing neurons that grow, differentiate, and live in vitro for as long as 10 weeks. These central nervous system cells form a confluent cell culture in which about 80% of the cells are fully differentiated neurons producing interconnecting axons and dendrite processes and live upon a sparse underlying population of fibrillary and protoplasmic astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and fibroblasts. Morphological and cytochemical characteristics of these cell types, based on immunofluorescent cell specific markers and silver staining of neurons, are presented.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulloch K., Stallcup W. B., Cohn M. The derivation and characterization of neuronal cell lines from rat and mouse brain. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambergs R., Leah J., Kidson C. Selection of differentiated neurons in embryonic mouse brain cultures using arabinofuranosylcytosine. Exp Neurol. 1978 Apr;59(2):296–303. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey E. W., Nelson P. G., Schrier B. K., Breuer A. C., Ransom B. R. Neurons from fetal rat brain in a new cell culture system: a multidisciplinary analysis. Brain Res. 1975 Jun 6;90(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90679-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak L. P., Dahl D., Bignami A. Glial fibrillary acidic protein in reaggregating and monolayer cultures of fetal mouse cerebral hemispheres. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 21;150(3):631–637. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90828-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Weber K. Actin antibody: the specific visualization of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuko S., Kuromi H., Shimada Y. Isolation and culture of motoneurons from embryonic chicken spinal cords. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Auger J., Barber B. H., Edwards A. J., Walsh F. S., Crumpton M. J. Actin may be present on the lymphocyte surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4484–4488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Mirsky R., Fields K. L., Lisak R. P., Dorfman S. H., Silberberg D. H., Gregson N. A., Leibowitz S., Kennedy M. C. Galactocerebroside is a specific cell-surface antigenic marker for oligodendrocytes in culture. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Neale E., Henkart M., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. I. Morphology and intrinsic neuronal electrophysiologic properties. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1132–1150. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Hard C. C. Actin co-caps with concanavalin A receptors. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):695–697. doi: 10.1038/269695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Raiborn C. W., Jr Dissociation, fractionation, and culture of embryonic brain cells. Brain Res. 1969 Jan;12(1):180–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]