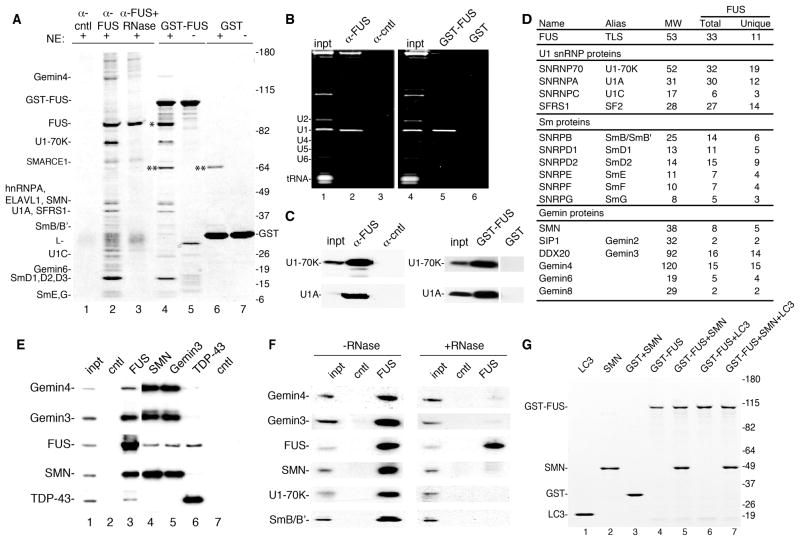
Fig. 1. The SMN complex and U1 snRNP associate with FUS.
(A) IPs were carried out with HeLa nuclear extracts using FUS or negative control antibodies (lanes 1–3). In lane 3, nuclear extract was incubated with RNase A prior to IP. GST-FUS (lanes 4 and 5) or GST (lanes 6 and 7) was used for pulldowns from nuclear extract (lanes 4 and 6) or buffer alone (lanes 5 and 7). Proteins were run on a 4–12% SDS gradient gel and detected by Coomassie. Indicated proteins were identified by mass spectrometry. L: antibody light chain. *: FUS, **: a non-specific band. (B) Total RNA from IP and GST pulldown samples used in panel A. 30% input (inpt) was loaded. RNAs were detected with ethidium bromide. (C). Protein was isolated from samples in panel B followed by Westerns using indicated antibodies. 15% input (inpt) was loaded. (D) Table showing mass spectrometry data for indicated proteins from FUS IP. The number of total peptides (Total) and total unique peptides (Unique) identified by mass spectrometry is shown. (E) IP/Westerns using indicated antibodies. The negative control for the FUS and TDP-43 antibodies was a rabbit polyclonal antibody (lane 2, SAP130), and the negative control for the monoclonal antibodies (SMN and Gemin3) was a monoclonal against HA (lane 7). (F) Same as panel E except nuclear extract was treated or not with RNase prior to the IP. (G) FUS interacts directly with SMN. The indicated purified proteins (2 μg) were mixed in the presence of RNase A followed by GST pulldowns. Proteins were separated on a 4–12% SDS-gradient gel and detected with Coomassie. Markers in kD are indicated.