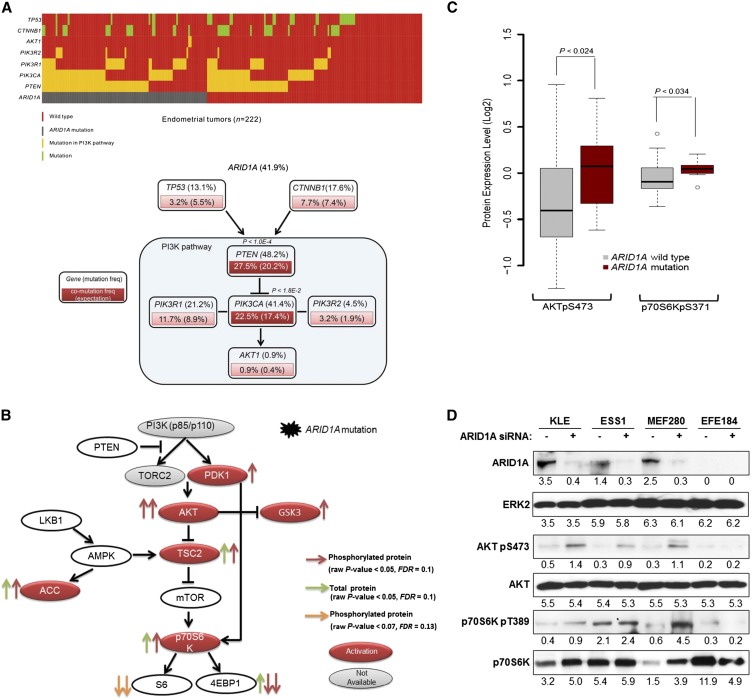
Figure 6.
Mutational and functional analysis of ARID1A on the activation of the PI3K pathway. (A) Co-mutation patterns of ARID1A and key genes related to the PI3K pathway. (Upper panel) Mutation diagram in the full set of endometrial tumor samples (n = 222). Each column represents a tumor, and each row corresponds to a single gene. (Lower panel) Mutation or co-mutation frequencies are expressed as a percentage of all the samples, and the co-mutation frequencies from random expectation are shown in parentheses for comparison. (Dark red) Genes with statistically significant co-mutations, accompanied with Bonferroni-corrected P-values. (B) The functional effect of ARID1A mutation on protein expression of the PI3K pathway. Each arrow represents a protein marker with significant differential expression between ARID1A wild-type and mutated samples: (red arrows) phosphorylated proteins and (green arrows) total proteins with P < 0.05 (two-sided t-test, FDR < 0.1); (orange arrows) phosphorylated proteins with marginal significance P < 0.07 (FDR < 0.13). (Solid red) Activated genes; (solid gray) genes without available protein expression data. (C) The functional effect of ARID1A mutation on the phosphorylation of AKT and p70S6K in tumor samples in which both PTEN and PIK3CA genes are wild-type, and also PTEN expression is retained (n = 47). P-values were calculated based on a two-sided t-test. (Boxes) The distribution of individual values from the lower 25th percentile to the upper 75th percentile; (solid line in the middle) median values; (lower and upper whisker) fifth and 95th percentiles; (small circles) outlier data points. (D) Four endometrial cancer cell lines were transfected with 20 nM ARID1A siRNA or nonspecific siRNA and harvested after 72 h for Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Numerical values below each lane of the immunoblots represent the quantification of the relative protein level by densitometry.