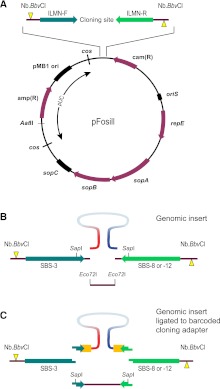
Figure 1.
pFosill cloning vectors. (A) General map of the pFosill family of modified pFOS1 Fosmid vectors. The cloning site for inserting the genomic DNA fragments is flanked by forward and reverse Illumina-primer sequences (ILMN-F and ILMN-R) and two Nb.BbvCI nicking endonuclease sites. Nicks (yellow triangles) are introduced on two different strands and are located 5′ of the cloning site. ILMN-F is the standard Illumina sequencing primer SBS-3. The reverse primer in pFosill-1 and pFosill-3 is the SBS-8 primer for standard paired-end sequencing. In pFosill-2 and pFosill-4, the reverse primer is SBS-12 for three-read multiplex paired-end sequencing. The pUC-derived portion between the two cos sites is not present in the final circularized Fosmids which replicate under the control of oriS and the F-factor functions repE and sopA-C that ensure proper partition of the Fosmid among the two daughter cells. Vectors are cut at the unique AatII site as well as two restriction sites at the cloning site and dephosphorylated. (B) Cloning site of pFosill-1 (SBS-8 version) and pFosill-2 (SBS-12). Sheared, end-repaired, and size-selected genomic insert fragments are inserted by blunt-end ligation between two dephosphorylated Eco72I sites 4 bp downstream from the ILMN sequencing primers. The SapI sites shown are not useful for cloning as pFosill-1 and -2 harbor three additional SapI sites. (C) pFosill-3 (SBS-8 version) and pFosill-4 (SBS-12) are digested with SapI which excises a single fragment that includes the 3′ ends of the sequencing primers. Sheared and end-repaired genomic insert fragments are ligated to an excess of adapters that provide an 8-bp barcode (orange), the 3′ end of the Illumina sequencing primers, and three non-self-complementary 5′ overhanging bases for sticky-end ligation to the SapI ends of the vector arms. Supplemental Table S1 summarizes the relevant features of all four pFosill vectors.