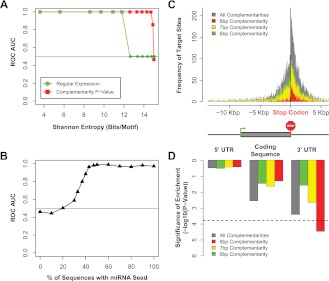
Figure 2.
The sensitivity and specificity of the miRvestigator algorithm and framework is estimated using simulated data sets. (A) The ROC AUC was computed by simulating miR-1 motifs across a range of motif entropies. Shown are the ROC AUC for the consensus matched to 8-bp miRNA seed sequences from miRBase using regular expression and the miRvestigator HMM-derived scoring metrics Viterbi P-value. (B) We then tested the sensitivity and specificity of coupling de novo motif detection algorithm Weeder to the miRvestigator (Fig. 1) by applying them to 30 simulated sequences with varying levels of inserted miR-1 seed sequence (0%–100%). (C) Histogram of Weeder-identified miRNA-binding sites for whole transcripts where transcripts are centered on the stop codon (0 bp). Instances of miRNA-binding sites were either stratified based upon their complementarity to the motif identified by Weeder (8, 7, or 6 bp) or the combination of all complementarities. As described by the gene structure below the histogram upstream of the stop codon are the 5′ UTR and coding regulatory regions, and downstream is the 3′ UTR. In the gene structure below the histogram, the coding sequence is a wider gray box, the start codon is a green arrow, and the stop codon is a red stop sign. (D) Significance of the enrichment of miRNA-binding sites per 1 Kbp was computed as a meta statistic and is shown for each gene region and each stratified site complementarity.