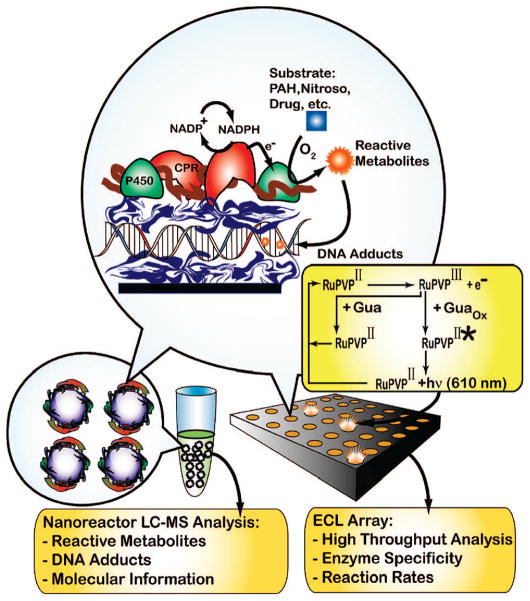
Scheme 1. Microsome/DNA Films and Reactions on Nanoreactors (Left) or Array Chip (Right)a.
a A layer of cationic polymer is initially deposited (blue ribbon in circle, e.g., poly(ethyleneimine (PEI) or [Ru(bpy)2PVP10]2+ (RuPVP), where bpy = bipyridine) followed by layers of negative DNA, polycation, and microsomes (membrane is brown, CPR = red, and cyt P450 = green). NADPH generated by an enzyme reaction in solution reduces CPR, which transfers electrons to cyt P450s. O2 and Cyt P450s can combine to convert substrate to reactive metabolites that form DNA adducts in the film. ECL is detected with a CCD camera on the array upon application of +1.25 V vs Ag/AgCl and monitors DNA adduct accumulation. Hydrolysis releases labile DNA adducts from the nanoreactors for capLC–MS analysis.