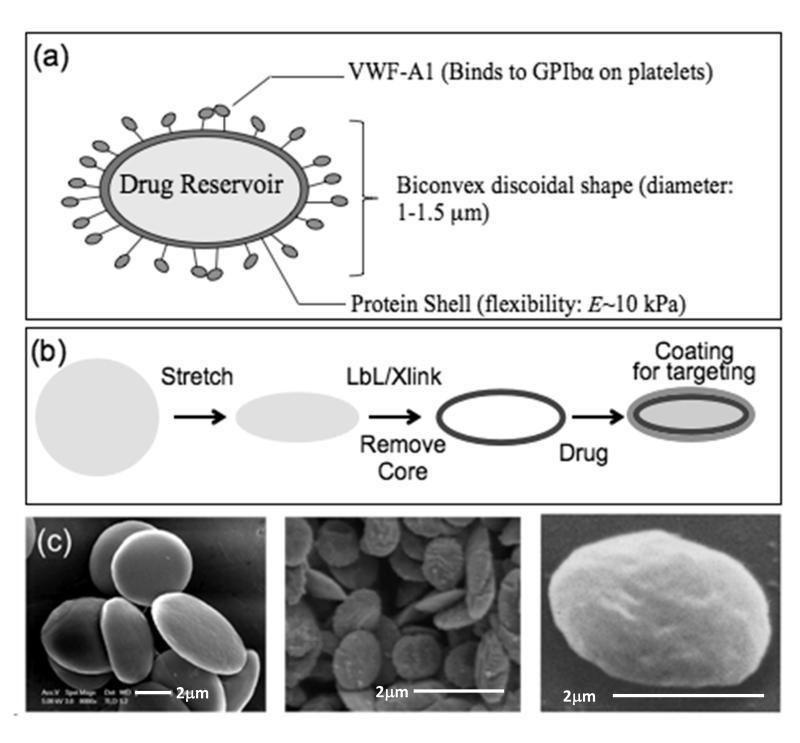
Figure 1. Fabrication of synthetic platelets.
(a) Schematic representation of a synthetic platelet (SP) coated with VWF-A1 targeting drug delivery to platelets. (b) Sequential steps in SP fabrication. Spherical polymeric particles are first stretched into oblate ellipsoids. Proteins and polyelectrolytes are then coated on the templates using layer by layer technique followed by crosslinking of the layers and dissolution of the polymeric core to obtain SPs, which can then be loaded with drugs and coated with fluorophores and targeting ligands. (c) Scanning electron microscopy images showing (from left to right) oblate ellipsoidal polymeric templates; SPs; and natural platelets (reproduced from Ref. [26]).