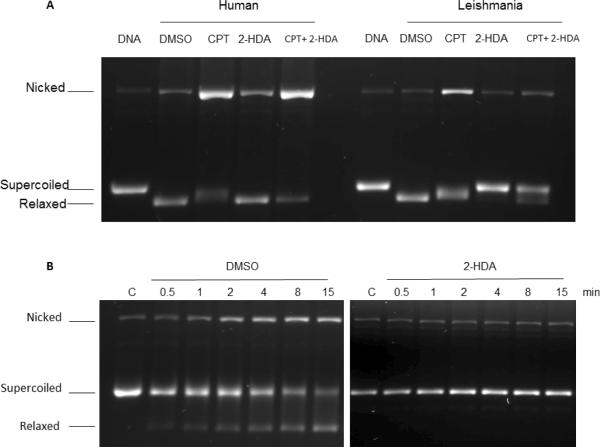
Figure 4.
Supercoiled plasmid DNA TopIB-mediated cleavage assay comparing the inhibition and poisoning of recombinant hTopIB (A left) and LdTopIB (A right) by 2-HDA and CPT. Both enzymes were assayed in the presence of DMSO (drug vehicle), 100 μM CPT (positive control for cleavage stabilization), 100 μM 2-HDA and a mix of 100 μM 2-HDA/CPT. Samples were incubated for 4 min at 25 °C, stopped with 1% SDS and digested for one extra hour at 37°C in the presence of 1 mg/ml proteinase K. DNA was extracted with one volume of phenol-chloroform and samples were run on a 1% agarose gel containing ethidium bromide to a final concentration of 40 μg/ml in order to separate supercoiled and relaxed DNA. The bottom figure (B left panel) shows that a pre-incubation (15 min at 4 °C) with DMSO had no influence on the CPT inhibiting/poisoning mechanism, as the nicked DNA band increased its relative intensity with respect to the control, at different time intervals. When LdTopIB was pre-incubated with a 2-HDA excess (100 μM) previous to the addition of 0.5 μg of pSK DNA the enzymatic activity was fully inhibited by 2-HDA and CPT poisoning effect did not take place (B right panel). After the time-course assay samples were extracted and run as previously described in 4A. The nicked band corresponds to the stabilized cleavage complexes. The results are representative of three independent trials.