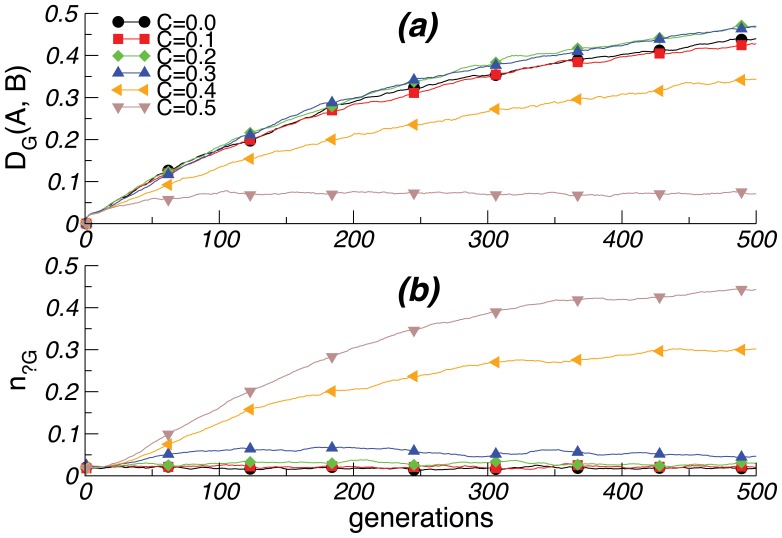
Figure 2. Interaction between subpopulations.
(a) C controls the probability that the fitness is determined by an individual’s ability to learn the language of the other population. We assume slow language change (l = 10−3; other parameters as in Figure 1). When C = 0, language is a stable target for the genes and the two subpopulations diverge genetically, with few neutral alleles. (b) As C increases, neutral genes predominate, and the subpopulations are genetically similar. The panel shows a single subpopulation.