Figure 3.
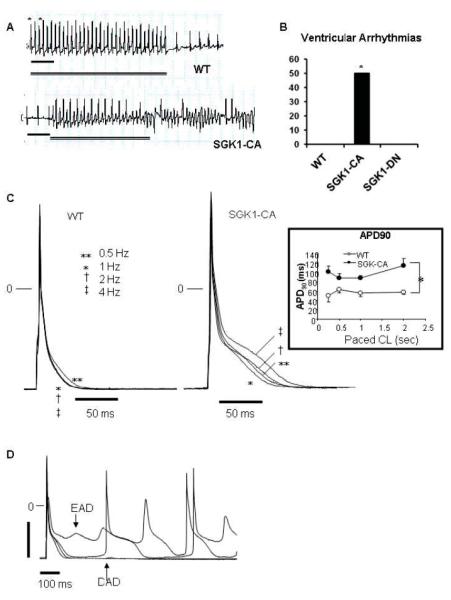
Propensity to ventricular arrhythmias, action potential prolongation, and afterdepolarizations are increased in SGK1-CA mice. (A) Representative tracings for WT and SGK1-CA mice from the distal (RV) pole during rapid pacing protocol (with pacing cycle lengths [CL] down to 60 msec in WT mice and 90 msec in the SGK1-CA mice). Asterisks denote pacing, double line indicates duration of pacing and scale bar denotes 200 msec. (B) Cumulative results for VT/VF inducibility from age-matched WT (0/5), SGK1-CA (3/6) and SGK1-DN (0/4) mice are shown (*p<0.05 by Z-test of proportions), in the absence of fibrosis or structural abnormalities (Supplemental Fig. S3). (C) Superimposed action potentials (APs) at CL 0.5-4 Hz in WT and SGK1-CA ventricular cardiomyocytes. Inset: APD at 90% repolarization (APD90) was longer in SGK1-CA compared with WT ventricular CMs, *p<0.05 by repeated measures ANOVA. (D) Representative EADs or DADs in SGK1-CA myocytes paced at 0.5 Hz. For quantification of EADs/DADs in comparison to WT see Fig. 5D.
