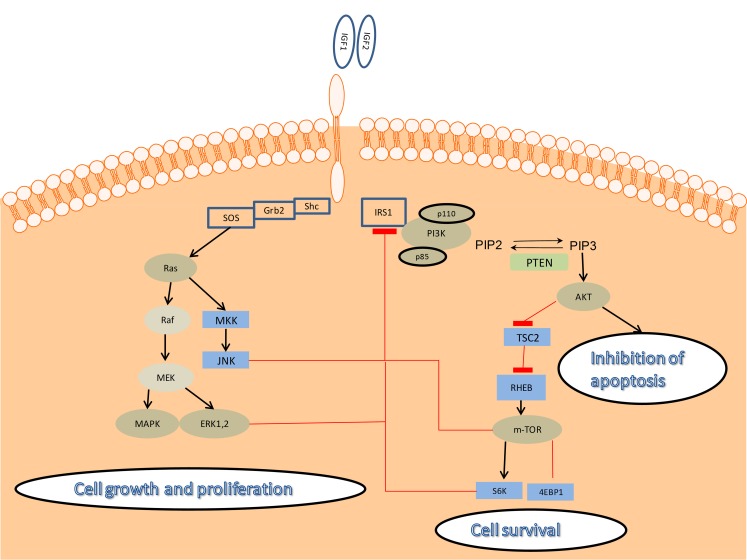
Fig. 1.
Downstream signaling of the IGF-1R. IGF-1R is a transmembrane tyrosine-kinase receptor, binding either IGF1 or IGF2. Ligand binding leads to IRS phosphorylation and recruitment of regulatory (p85) and catalytic (p110) subunits of PI3K and subsequently Akt phosphorylation on threonine 308. Serine 473 of Akt is phohoshorylated by mTORC2 complex also activated by IGF-1R by an unknown mechanism. Akt promotes cell survival by multiple mechanisms, inhibiting apoptosis and inducing expression of prosurvival genes. The other parallel pathway, related to IGF-1R by IRS or Shc proteins is the RAS-RAF-MAPK and JNK, resulting in cell proliferation. Negative regulation by mTORC1, S6K, JNK and ERKs induces IRS1 degradation. ( AKT—protein kinase ; ERK—extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; MAPK—mitogen activated protein kinase; Grb2—growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; IGF-1R—insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; GSK3—glycogen synthase kinase 3; IRS 1—insulin-like receptror substrate 1; MEK—mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR—mammalian target of rapamycin, PI3K—phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PIP2—phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate; PIP3—phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 triphosphate; PTEN—phosphatase and tensin homolog; RHEB—Ras homolog enriched in brain; S6K—S6 kinase; SOS—son of sevenless; TSC2—tuberous sclerosis complex 2)