Figure 6.
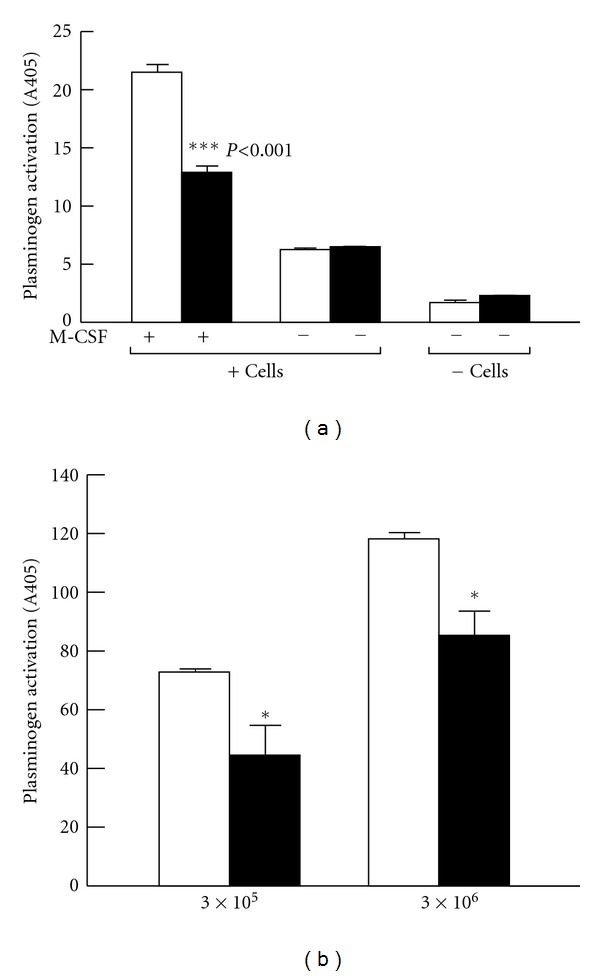
(a) Plg-RKT regulates cell surface plasminogen activation by t-PA. Plasminogen activation was determined after adding 2.7 μM Glu-plasminogen and 20 nM single chain recombinant t-PA in either the presence or absence of either undifferentiated Hoxa9-ER4 progenitor cells or M-CSF-differentiated Hoxa9-ER4 cells and in the presence of either rat anti-Plg-RKT mAb35B10 (filled bars) or isotype control rat IgG2a (open bars). ***P < 0.001, compared to the corresponding isotype control. This research was originally published in [18]. (b) Plg-RKT regulates cell surface plasminogen activation by uPA. Plasminogen activation was determined in the presence of different concentrations of U937 cells, as indicated, and in the presence of 2.7 μM Glu-Plasminogen and 20 nM uPA and in the presence of 170 nM of either anti-Plg-RKT mAb7H1 (filled bars) or mouse IgG2a isotype control (open bars). Cell-dependent plasminogen activation on the tripeptide substrate, S2251, is shown after subtracting plasminogen activation in the absence of cells. **P < .001 compared with the corresponding isotype control. This research was originally published in [20].
