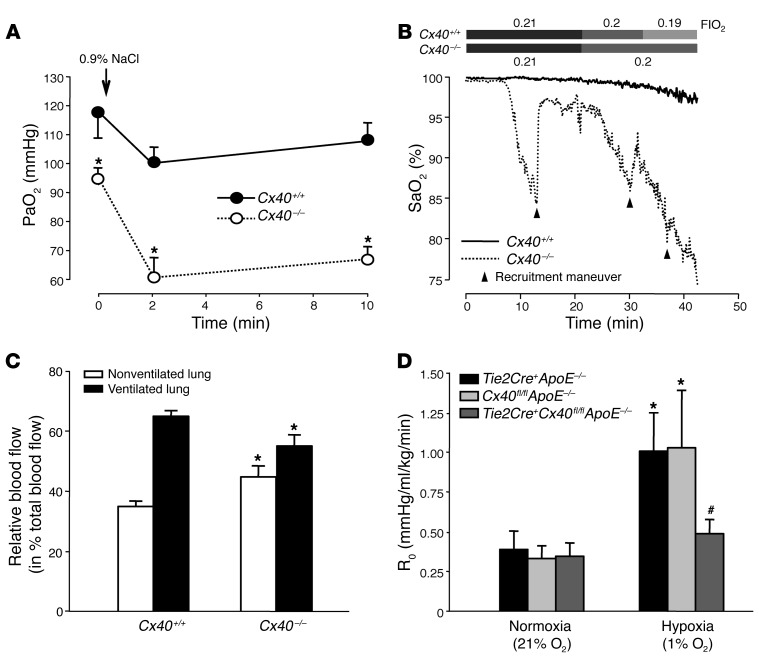
Figure 4. Cx40 optimizes oxygenation and V/Q matching in hypoxic lungs in vivo.
(A) Group data (n = 5 lungs each) showing arterial PaO2 in anesthetized Cx40+/+ and Cx40–/– mice prior to (0 minutes) and after partial occlusion of larger airways by tracheal instillation of 25 μl saline. PaO2 was already significantly lower in Cx40–/– versus Cx40+/+ mice at baseline; this difference was further amplified after induction of V/Q mismatches by saline instillation. *P < 0.05 vs. Cx40+/+. (B) Representative tracings (of 5 replicates) showing SaO2 in anesthetized Cx40+/+ and Cx40–/– mice during stepwise decrements in FIO2 starting at 0.21. In the case of sudden SaO2 decrements, recruitment maneuvers were performed (arrowheads) to counteract atelectases. (C) Group data (n = 5 lungs each) showing relative blood flow (percent total pulmonary blood flow) to the nonventilated right and ventilated left lung during 1-lung ventilation in Cx40+/+ and Cx40–/– mice, assessed by fluorescent microsphere technique. *P < 0.05 vs. Cx40+/+. (D) Group data (n = 5 lungs each) showing acute HPV response, determined as R0 10 minutes after hypoxia (1% O2) onset versus normoxia (21% O2), in isolated perfused lungs of Tie2Cre+Cx40fl/flApoE–/– mice and Tie2Cre+ApoE–/– and Cx40fl/flApoE–/– controls. *P < 0.05 vs. normoxia; #P < 0.05 vs. Tie2Cre+ApoE–/– and Cx40fl/flApoE–/–.