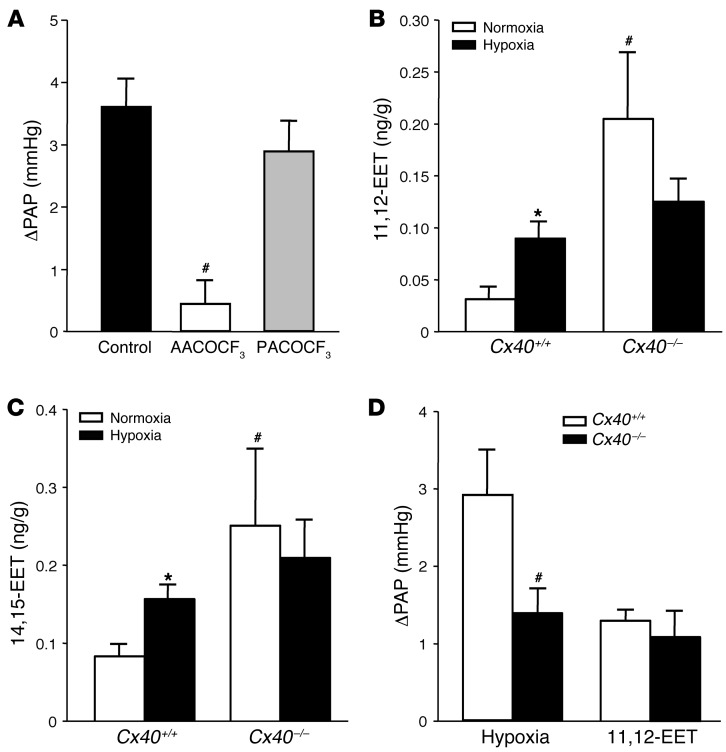
Figure 9. Role of cPLA2 and EETs in acute HPV.
(A) Group data (n = 5 lungs each) showing acute HPV response, determined as ΔPAP 10 minutes after hypoxia onset (1% O2) versus normoxia (21% O2) in untreated isolated perfused lungs of Cx40+/+ mice (control) and in lungs of Cx40+/+ mice treated with either the cPLA2-specific inhibitor AACOCF3 or the iPLA2-specific inhibitor PACOCF3 (both 1 μM). #P < 0.05 vs. control. Group data showing concentrations of (B) 11,12-EET and (C) 14,15-EET in isolated lungs of Cx40+/+ and Cx40–/– mice lungs at normoxia or after 10 minutes of hypoxia. *P < 0.05 vs. normoxia; #P < 0.05 vs. Cx40+/+. (D) Group data (n = 5 lungs each) showing acute pulmonary vasoconstrictor response to hypoxia and exogenous infusion of 11,12-EET (3 μM), determined as ΔPAP, in isolated lungs from Cx40+/+ and Cx40–/– mice. #P < 0.05 vs. Cx40+/+.