Fig. 8.
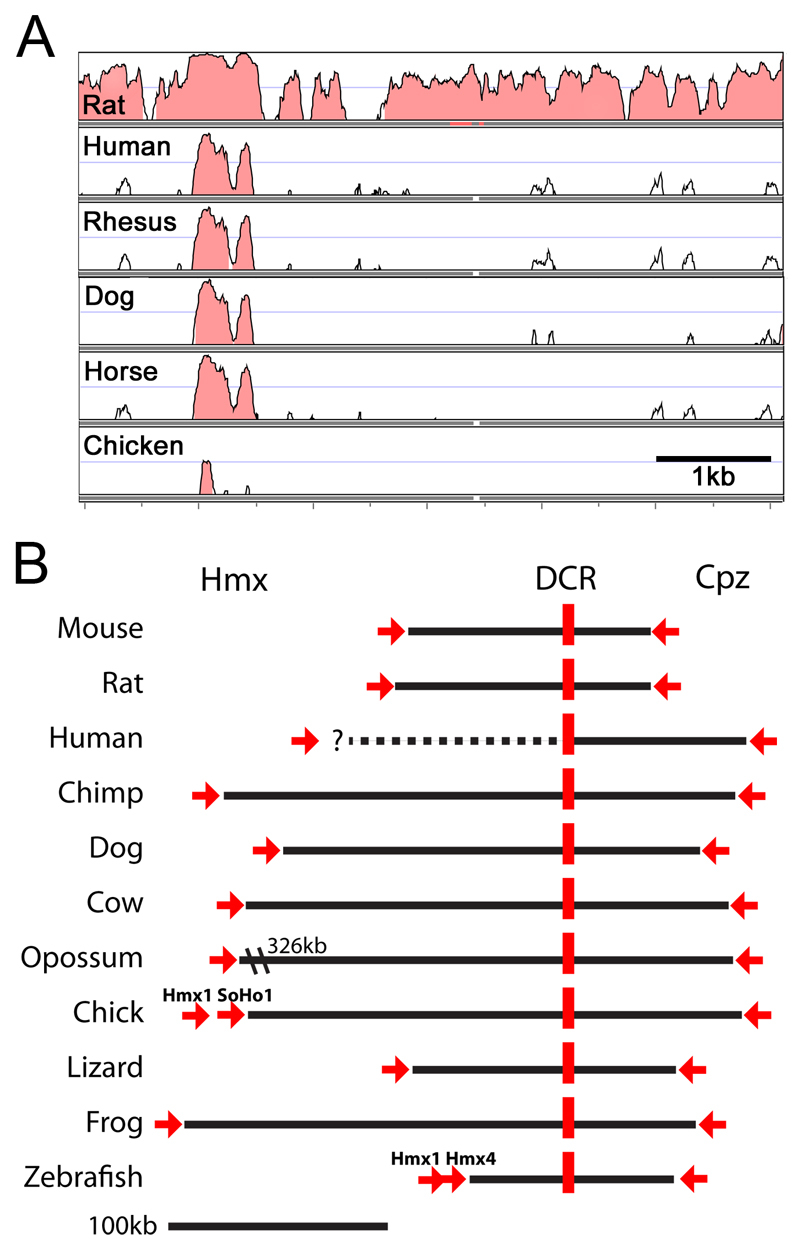
Comparative genomics of the Hmx1 distal conserved region. (A) VISTA alignment of the dmbo deletion region. The reference sequence for the alignment is chr5:35,807,810-35,813,977 (version NCBI37/mm9) of the mouse genome. A highly conserved region of ∼500 bp is detected across all mammalian species, and a core sequence is conserved across vertebrate classes. (B) Map of the relationship of the DCR to Hmx and Cpz genes for all vertebrate species for which contiguous genomic sequence is available. Red arrows indicate the 3× end of the actual or predicted Hmx1 and Cpz transcripts, and the direction of transcription. The distance from Hmx1 to the DCR in the human genome is unknown because of a gap in genomic coverage. The chick genome contains two Hmx1 homologues, Hmx1 and SOHo1, transcribed on the same strand; similarly, the zebrafish genome contains two Hmx1 homologues, Hmx1 and Hmx4. For each species, the genome build version and genomic coordinates of the core conserved sequence (∼300 bp) are as follows: Mouse, mm9, chr5:35,808,825-35,809,130; Rat, rn4, chr14:80,916,323-80,916,629; Human, hg18, chr4:8,753,059-8,753,365; Chimp, panTro2, chr4_random:6,195,662-6,195,968; Dog, canFam2, chr3:63,192,444-63,192,750; Cow, bosTau3, chr6:108,192,356-108,192,675; Opossum, monDom4, chr5:228,001,978-228,002,289; Chick, galGal3, chr4:84,267,370-84,267,675; Lizard, anoCar1, scaffold_326:1,558,135-1,558,406; Frog, xenTro2, scaffold_583:238,403-238,706; Zebrafish, danRer7, chr1:41,246,062-41,246,105.
