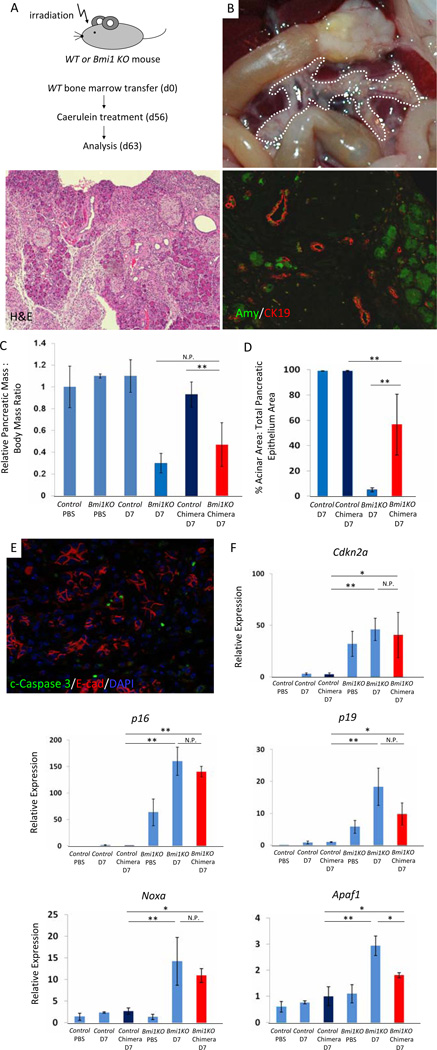
Figure 6. Hypoplastic pancreas and impaired exocrine pancreas regeneration are mediated through a combination of cell autonomous and non-cell autonomous mechanisms in Bmi1 KO mice after caerulein pancreatitis.
(A) Experimental outline. Wild-type bone marrow was transplanted into irradiated wild-type or Bmi1 KO mice at 6–8 weeks. 8 weeks after bone marrow transplantation, reconstituted Bmi1 KO chimera and wild type mice were subjected to caerulein pancreatitis and were sacrificed 7 days after treatment.
(B) Macroscopic view of the pancreas reveals moderate pancreatic hypoplasia in reconstituted Bmi1 KO chimera mice 7 days after caerulein treatment. H&E stain and Co-staining for amylase/CK19 show exocrine pancreas regeneration is partially impaired in reconstituted Bmi1 KO chimeric mice 7 days after caerulein treatment.
(C) Relative pancreatic weight normalized to body weight. N = 3 to 6 mice. Means ± SD. Quantification of acinar regeneration. N = 3 or 4 mice. Means ± SD. Co-staining for cleaved Caspase 3/E-cadherin/DAPI in reconstituted Bmi1 KO chimeric mice reveals presence of apoptotic cells 7 days after caerulein treatment.
(D) Relative expression levels of Cdkn2a, Noxa, and Apaf1 in the pancreas by q-PCR analysis. N = 3 or 4 mice. Means ± SD. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. N.P. = not significant p value.