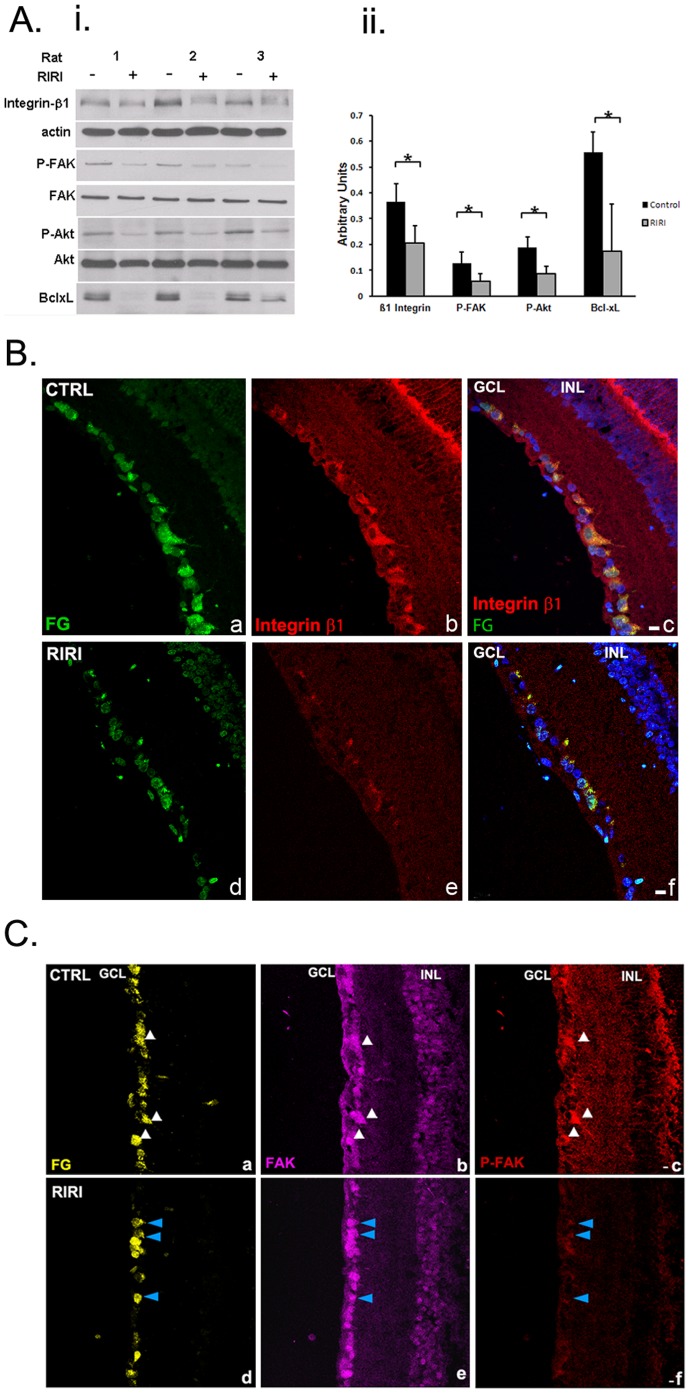
Figure 3. Integrin survival signaling is down-regulated in RGC in the retina 1 day after ischemic injury. A.
(i ) Western blot of retinal extracts of ischemic, RIRI (+), and control (−) rat eyes 1 day post-injury (n = 3). A representative example of at least 5 independent experiments is presented. (ii) Densitometric analysis of western blotting with all samples normalized to β-actin. Error bars, SD. Student’s t test. *p<0.05. B. β1 integrin expression is decreased in RGC 1 day post-RIRI. Immunohistochemistry with β1 integrin antibodies (red) in frozen retinal sections from control (a, b, c), and ischemic retinas (d, e, f), in which RGCs were retrogradely labeled with FG (green; a, d) shows reduced β1 integrin expression in ischemic eyes in comparison with control eyes (red; b, e) specifically in RGC (yellow; merged; c, f). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue; c, f). (n = 12). GCL = ganglion cell layer, INL = inner nuclear layer. Scale bars: 10 µm. C. FAK activation is reduced in RGC 1 day after ischemia. Immunohistochemistry with FAK (purple), and P-FAK [pY397] (red) antibodies in frozen retinal sections of control (a, b, c), and ischemic retinas (d, e, f) at 1 day post-RIRI, in which RGCs were retrogradely labeled with FG (yellow; a, d) shows significantly decreased expression of the activated, phospho [pY397] FAK in ischemic eyes in comparison with control eyes (red; c, f), while FAK expression remains unchanged (purple; b, e). White arrows identify FG labeled RGCs in the control retina (CTRL) expressing high levels of both FAK, and P-FAK [pY397] (a, b, c). Blue arrows point toward RGCs in the ischemic retina (RIRI) that have markedly decreased expression of P-FAK [pY397], while FAK expression is the same (d, e, f). (n = 12). GCL = ganglion cell layer, INL = inner nuclear layer. Scale bars: 10 µm.