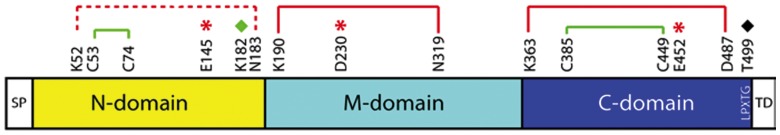
Figure 1. Domain architecture of FimP.
The FimP protein is comprised of a signal peptide (SP), an N-terminal domain, a middle domain and a C-terminal domain followed by an LPXTG motif and a transmembrane domain (TD). Residues involved in isopeptide and disulfide bonds are illustrated with bars and stars, in red and green, respectively. A lysine and a threonine involved in pili polymerization are illustrated with a green and black diamond respectively.