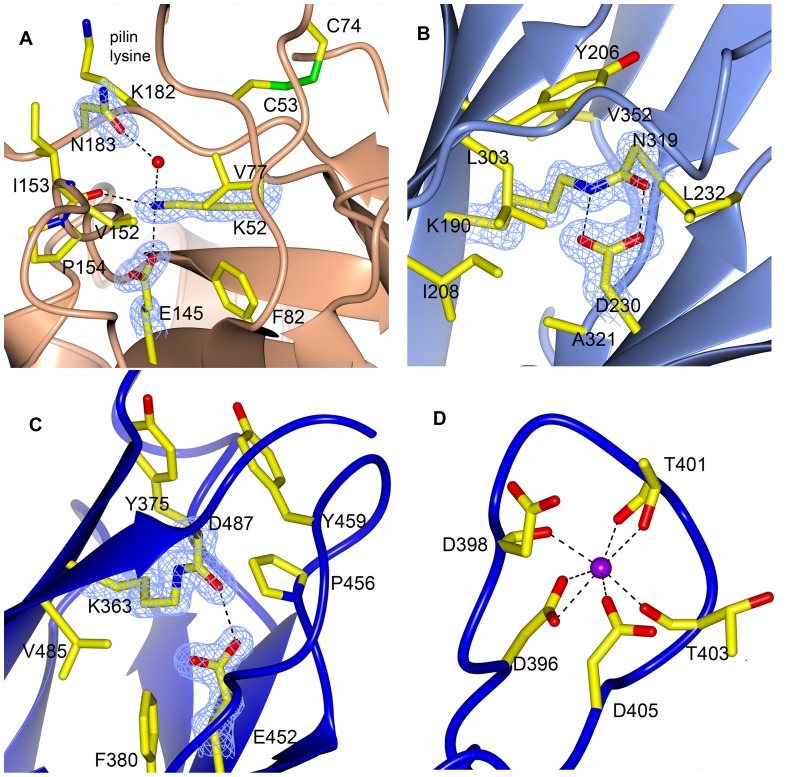
Figure 4. Stabilizing isopeptide bonds (formed and unformed) and a metal binding loop.
A: The putative isopeptide residues in the N-domain, Lys-52, Asn-183 and Glu-145, do not form an isopeptide bond in the crystal structure. B: The M-domain isopeptide bond formed between Lys-190 and Asn-319 with the catalytic Asp-230. Asp-230 forms a bidentate hydrogen bond with the isopeptide bond. C: The C-domain isopeptide bond formed between Lys-363 and Asp-487 with the catalytic Glu-452. Glu-452 forms one hydrogen bond with the isopeptide bond carbonyl oxygen. D: A Ca2+ ion is coordinated by five residues of a loop that protrudes from the C-domain. Residues involved in isopeptide bond formation are represented as stick models, colored by atom type in a simulated annealing, omit Fo-Fc maps contoured at 4σ. Hydrogen bonds are shown as broken lines. Surrounding hydrophobic residues are shown as stick models.