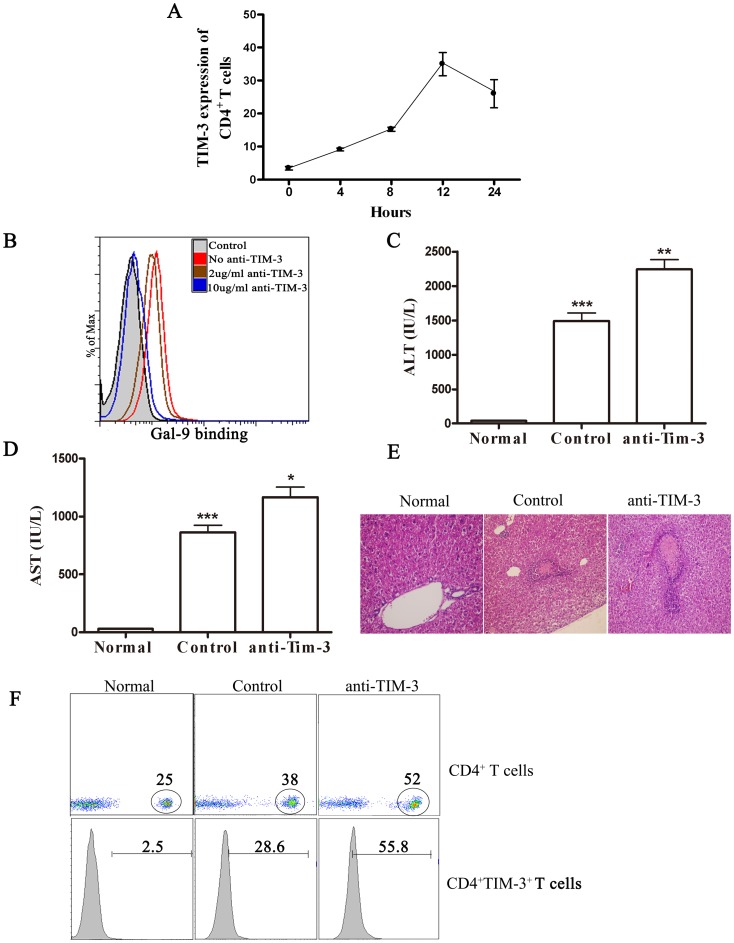
Figure 2. Effect of TIM-3 blockade on liver inflammation and CD4+ T cell immune response.
Isotype or TIM-3 mAb (100 µg per mouse) was administrated i.v. to Balb/c mice (n = 8 per group) 30 min before Con A injection (20 mg kg–1). (A) TIM-3 expression of CD4+ T cell in spleen was detected 24 h following Con A injection. (B) The effect of anti-TIM-3 on the binding of galectin-9 to mouse Th1 cells. CD4+ T cells were purified from splenocytes of normal mice by negative selection with magnetic beads. Cells (1×106 cells/ml) were cultured for 5 d with phytohemagglutinin (1 mg/ml) and IL-2 (8 ng/ml) in polarizing conditions: IL-12 (2 ng/ml) plus antibody to IL-4 (anti-IL-4; 100 ng/ml; MP4-25D2); Cells (5×105 cells/ml) were collected and incubated for 1 h at 4°C with biotinylated galectin-9 in the presence or absence of increasing anti-TIM-3 (2 ug/ml or 10 ug/ml). Cells were then incubated for 45 min at 4°C with fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated streptavidin, were washed and were analyzed by FACS. Serum ALT (C) and AST (D) levels were measured 24 h after Con A injection. The results were presented as the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. **, p<0.01; *, p<0.05. (E) The livers were removed 24 h later. Paraffin sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Representative liver sections were shown for each group, original magnification: ×200. (F) Percentages and phenotype (surface TIM-3) of CD4+ T cells in spleen of mice are shown. Normal, normal mice; Control, PBS treatment in Con A-treated mice; anti-TIM-3, anti-TIM-3 mAb pretreatment in Con A-treated mice.