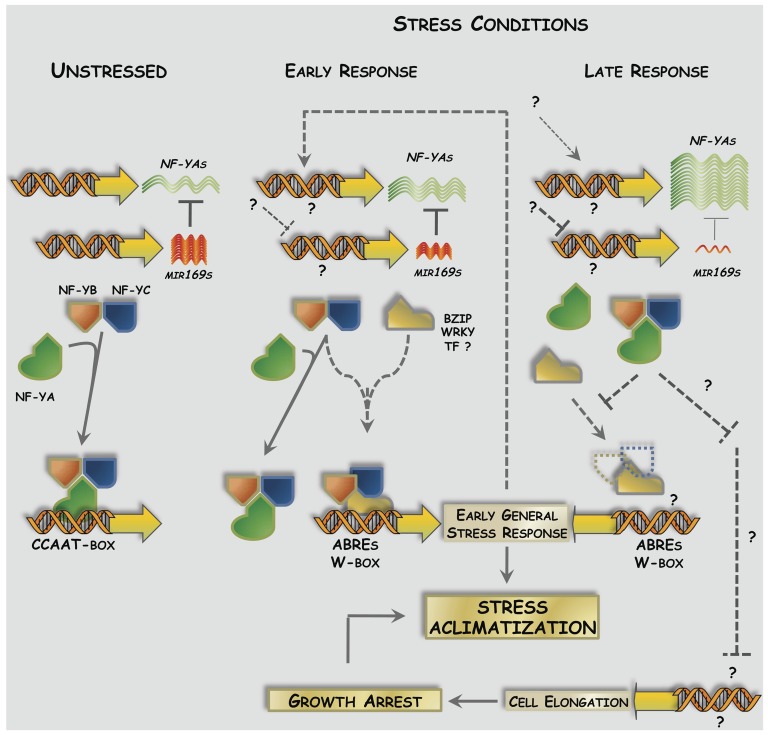
Figure 11. Hypothetical Molecular Model of NF-YA action mode.
In WT plants growing under non-stress conditions, the expression of NF-YAs is low due miR169-mediated post-transcriptional down-regulation, but sufficient to activate the transcription of CCAAT-box containing promoters. Upon exposure to abiotic stress, NF-YA levels increase due to the transcriptional activation of NF-YA expression (early) and to the repression of miR169 (late). NF-YAs repress early general stress response genes sequestering NF-YB/NF-YC heterodimer avoiding its interaction probably with bZIPs, and on the other hand, participating in the late down-regulation of cell wall remodeling genes. This last step could be responsible of growth arrest mediated by these TFs when plants face for long time a stressful environment.