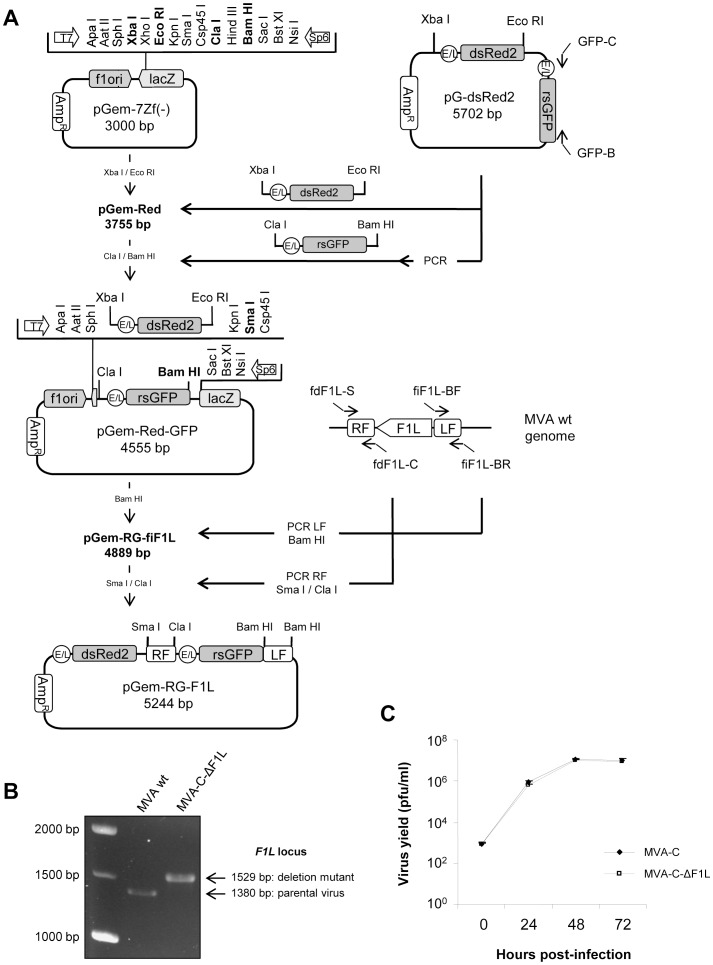
Figure 1. Generation and in vitro characterization of MVA-C-ΔF1L deletion mutant.
(A) Scheme of construction of the plasmid transfer vector pGem-RG-F1L. The plasmid transfer vector pGem-RG-F1L was obtained by sequential cloning of markers dsRed2 and rsGFP and F1L recombination flanking sequences into the plasmid pGem-7Zf. The dsRed2 gene under the control of the synthetic early/late (E/L) promoter was excised from plasmid pG-dsRed2 and inserted into pGem-7Zf to generate pGem-Red. The rsGFP gene under the control of the synthetic E/L promoter was amplified by PCR from plasmid pG-dsRed2, digested and inserted into the plasmid pGem-Red to generate pGem-Red-GFP. MVA genome was used as template to amplify the left flanking sequence of F1L gene. The PCR product was digested and inserted into pGem-Red-GFP previously digested and dephosphorylated by incubation with Calf intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase (CIP) to generate the plasmid pGem-RG-fiF1L. The right flanking sequence of F1L gene was amplified by PCR from MVA genome. The PCR product was digested and inserted into plasmid pGem-RG-fiF1L to generate the plasmid transfer vector pGem-RG-F1L. (B) Confirmation of F1L gene deletion by PCR analysis. Viral DNA was extracted from DF-1 cells infected with MVA wt or MVA-C-ΔF1L at 5 PFU/cell. Primers fdF1L-S and fiF1L-BR spanning F1L flanking sequences were used for PCR analysis of F1L locus. In parental MVA, a 1380 bp-product is obtained while in deletion mutant a unique 1529 bp-product is observed. (C) Analysis of virus growth of MVA-C-ΔF1L in CEF cells. Monolayers of CEF cells were infected with MVA-C or MVA-C-ΔF1L at 0.01 PFU/cell. At different times post-infection (0, 24, 48 and 72 hours), cells were collected and infectious viruses were quantified by immunostaining assay.