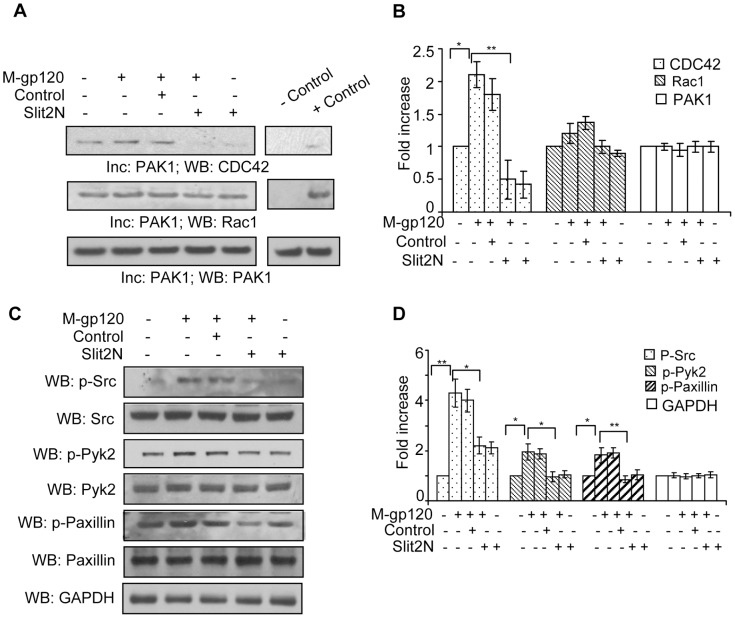
Figure 6. Slit2N inhibits M-gp120-induced signaling through Src, and activation of Pyk2, CDC42, Rac1, and paxillin.
(A) CDC42 and Rac1 activation assay: Lysates of untreated iMDDCs, and iMDDCs incubated with M-gp120, Slit2 negative control then M-gp120, Slit2N then M-gp120, or Slit2N alone were incubated with activated PAK1-conjugated agarose. Binding of activated CDC42 and Rac1 to PAK1 was visualized by Western blot analysis as described in Materials and Methods. PAK1 used as loading control. Representative assay is shown. (B) Quantitative analysis of the CDC42 and Rac1 activation by Western blot analysis. The band intensity in each lane was determined by densitometry. The fold change was determined by calculating the value of each lane vs. the unstimulated control or as indicated. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments (*p<0.05, **p≤0.01). (C) Representative Western blot analysis of total and phosphorylated Src, Pyk2 and paxillin in untreated iMDDCs, and in iMDDCs incubated with M-gp120, Slit2 negative control then M-gp120, Slit2N then M-gp120, or Slit2N alone. GAPDH used as loading control. (D) Quantitative analysis of phosphorylated Src, Pyk2 and paxillin by Western blot analysis in untreated iMDDCs, and in iMDDCs incubated with M-gp120, Slit2 negative control then M-gp120, Slit2N then M-gp120, or Slit2N alone. GAPDH used as loading control. The band intensity in each lane was determined by densitometry. The fold change was determined by calculating the value of each lane vs. the unstimulated control or as indicated. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments (*p<0.05, **p≤0.01).