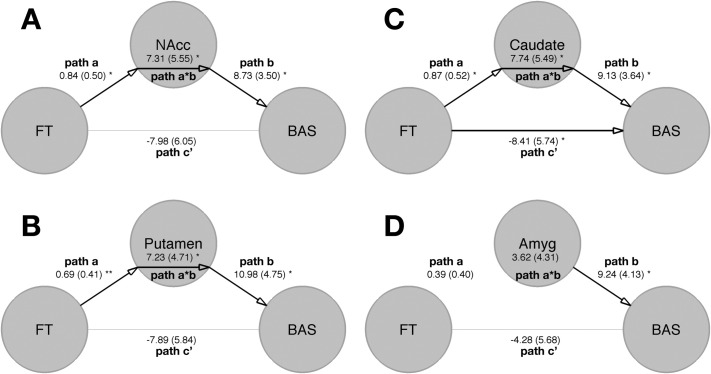
Figure 3.
Path diagrams of relationships between fetal testosterone (FT), neural mediators in the striatum or amygdala, and total behavioral approach system (BAS) score summing across all subscales. (A) Path diagram when nucleus accumbens (NAcc) Happy > Fear response is the mediator between FT and BAS. (B) Path diagram when putamen Happy > Fear response is the mediator between FT and BAS. (C) Path diagram when caudate Happy > Fear response is the mediator between FT and BAS. (D) Path diagram when amygdala (Amyg) Happy > Fear response is the mediator between FT and BAS. Path a is the relationship between the predictor (FT) and the mediator (region of interest [ROI]). Path b is the relationship between the mediator (ROI) and the outcome (BAS), controlling for the predictor (FT). Path c' is the relationship between the predictor (FT) and the outcome (BAS) controlling for the mediator (ROI). Path c is the total effect of the relationship between the predictor (FT) and the outcome (BAS), irrespective of the mediator. Path a*b is the difference between path c and path c'. Path coefficients and standard errors (in parentheses) are noted for each path. *p < .05, **p < .01.