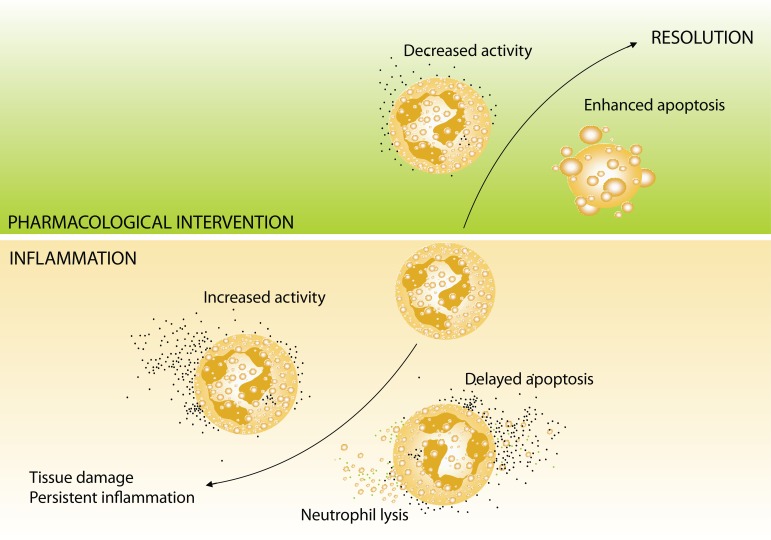
Figure 1.
Scheme illustrating the impact of neutrophils on the fate of inflammatory reaction. Prolonged or excessive formation and liberation of cytotoxic substances from neutrophils, along with delayed apoptosis of these cells, intensify inflammation and the risk of tissue damage. Pharmacological intervention, accelerating apoptosis and reducing activities of neutrophils, leads to resolution and contributes to termination of inflammatory reaction.