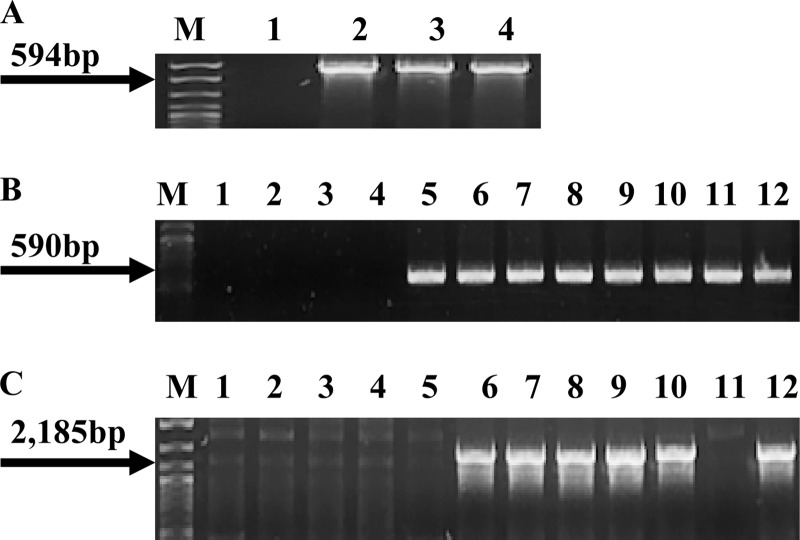
Fig 1.
Presence of cadA1, cadA2, and bcrABC in nonpathogenic donor strains. (A) PCR-based detection of cadA1 using the primers cadA-Tn5422F and cadA-Tn5422R. Lanes 1, 2, 3, and 4, L. innocua strains L0910, L0921, L1214B, and L1306A, respectively; lane M, DNA molecular marker XIV (Roche, Indianapolis, IN). The arrow points to the expected cadA1 PCR product. (B) PCR-based detection of cadA2 using the primers cadA-pLM80F and cadA-pLM80R. Lanes 1, 2, 3, and 4, L. innocua strains L0910, L0921, L1214B, and L1306A, respectively; lanes 5, 10, and 11, L. innocua strains CLIP 11262, L1221, and L1333a, respectively; lanes 6, 7, 8, and 9, L. welshimeri strains L0725, L1325, L0918, and L0926, respectively. Lane 12, L. monocytogenes H7550, used as a positive control (12). Lane M, same as in panel A. Arrow points to the expected cadA2 PCR product. (C) PCR of bcrABC using primers BcF and BcR. Lanes are as defined in panel B. With the exception of L. innocua strains CLIP 11262 and L1333a in lanes 5 and 11, respectively, all donors harboring cadA2 also contained bcrABC. Lane M, same as in panel A. Arrow points to the expected bcrABC product.