Figure 1.
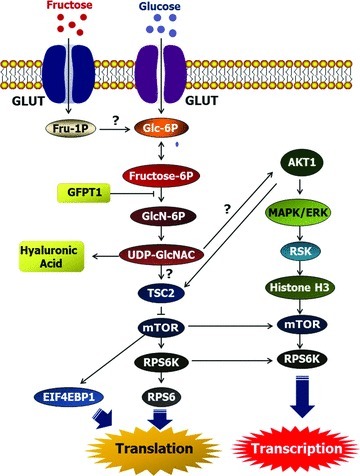
Schematic diagram of the glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 1 (GFPT1)–mediated MTOR signaling pathway affected by glucose and fructose in porcine trophectoderm cells. Available evidence from our study indicates that fructose and glucose are metabolized via GFPT1 in the hexosamine biosysthesis pathway and activate mTOR-RPS6K and mTOR-EIF4EBP1 signal transduction cascades for porcine trophoblast cell proliferation and mRNA translation, as well as synthesis of glycosaminoglycans such as hyaluronic acid. Fru, fructose; Glc, glucose; GLUT, glucose/fructose transporter; Glc-6P, glucose-6-phosphate; Fru-1P, fructose-1-phosphate; Fru-6P; GlcN-6P, N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate; UDP-GlcNAC, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine; GFPT1, glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 1; TSC2, tuberous sclerosis 2; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; RPS6K, ribosomal protein S6K; RPS6, ribosomal protein S6; EIF4EBP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; AKT1, protooncogenic protein kinase Akt; MAPK/ERK, mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
