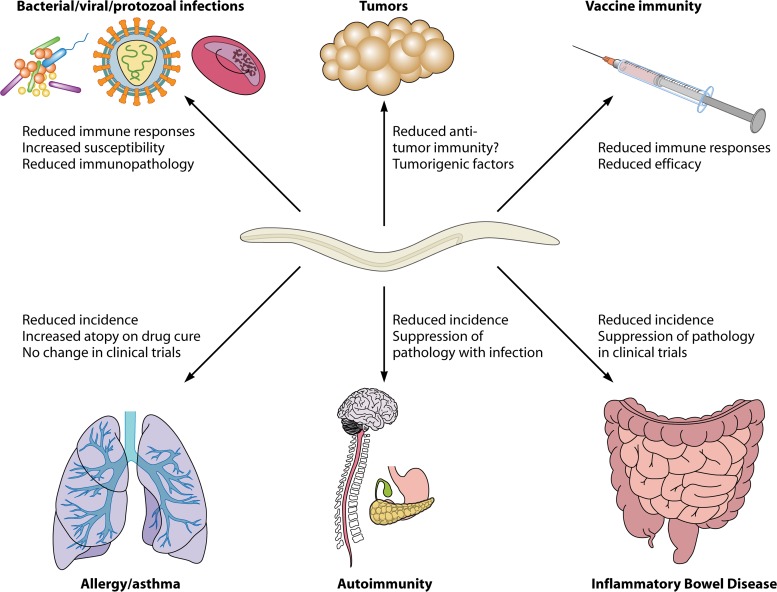
Fig 2.
Immunoregulatory effects of helminths on bystander responses. Helminths can suppress a wide range of bystander immune responses, including those of both immunopathogenic and protective natures. Coinfection with helminths suppresses antibacterial, antiviral, and antiprotozoal immunity, leading to increased susceptibility and attenuated immunopathology or, in some cases, exacerbated pathology due to higher infection burdens. Antitumor immunity may be suppressed by helminth infections, which may also release directly carcinogenic factors, potentially leading to increased numbers of malignancies in infected individuals. Vaccine efficacy is compromised by helminth infections due to suppressed immune responses. Immunopathologies such as asthma, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory bowel diseases are all reduced in prevalence in areas where helminth disease is endemic, and direct effects of helminth infections on the suppression of disease have been shown in clinical trials for inflammatory bowel diseases.