Fig 2.
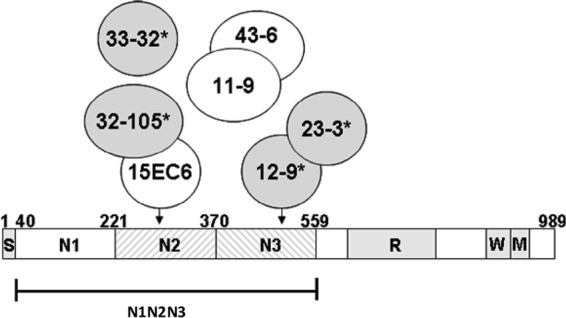
A subset of ClfA MAbs inhibit Fg binding. Schematic representation of S. aureus ClfA and the recombinant N1 to N3 vaccine antigen (rClfAm). S, signal peptide; N1 to N3 Fg-binding subdomains; R, serine-aspartate dipeptide repeat region; W, cell wall-spanning region; M, membrane-spanning region. Circles represent ClfA-specific MAbs that bind within the N2 and N3 domains. Their subdomain specificities, ClfA binding affinities, and abilities to interfere with S. aureus Fg binding are summarized in Table 1. Arrows reflect the specificities of MAbs 15EC6 and 12-9 for subdomain N2 and N3 epitopes. Intersecting circles indicate that epitopes recognized by MAbs overlap, as indicated by binding interference experiments (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). Four MAbs that prevent S. aureus Fg binding are shaded (with asterisks); three others are nonfunctional.
