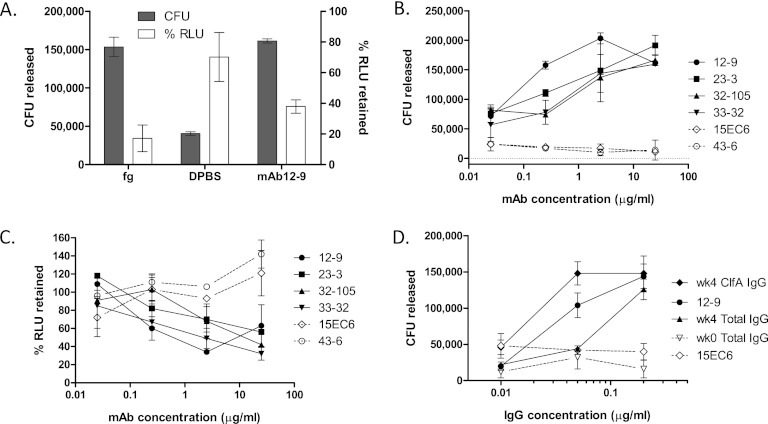
Fig 5.
S. aureus is released from immobilized Fg by free ligand or by functional antibodies. (A) Washed PFESA0237 bacteria bound to Fg-coated microplate wells were incubated with Fg (1 mg/ml), PBS, or MAb 12-9 (2.4 μg/ml) for 30 min at RT. After mixing, cells released by treatment were counted by CFU plating (shaded bars, numbers of CFU released) and the remaining adherent cells were quantified by luminescence detection with values normalized relative to those of untreated wells (open bars, percentage of relative light units [RLU] retained). (B) Bacterial release following treatment with 10-fold dilutions of ClfA MAbs. Antibodies that are active in the Fg binding inhibition assay (closed symbols, Table 1) also reverse binding in a concentration-dependent manner. Inactive MAbs (open symbols, dotted lines) fail to release bound cells. (C) Companion luminescence data measuring bound cells remaining following MAb treatment and washing. (D) The activity of total IgG and ClfA-IgG purified from vaccinated (week [wk] 4) donors in releasing bacteria (in this case, PFESA0172) is compared with that of MAb 12-9. ClfA-IgG was purified from the total IgG pool by antigen affinity chromatography with recovery of 1.3%. Concentration-dependent release of bacteria was not observed with IgG purified from prevaccinated subjects (week 0) or with nonfunctional MAb 15EC6. Similar results were obtained in an independent experiment. Error bars represent standard deviations of duplicate samples.