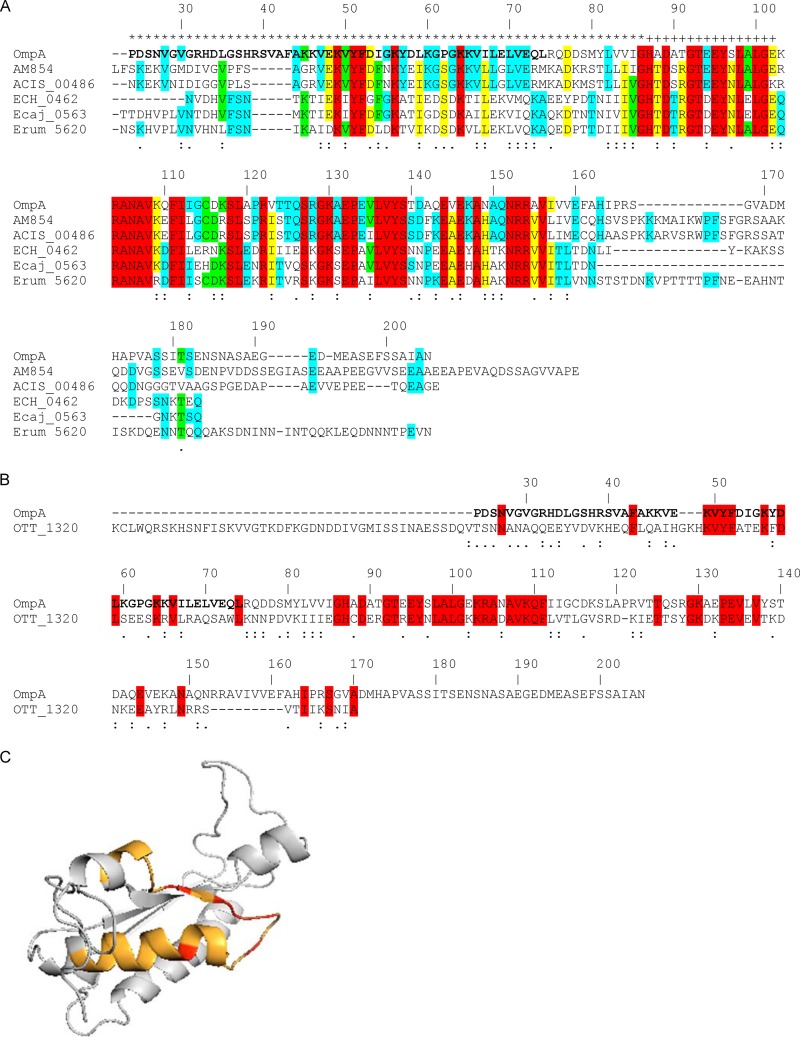
Fig 6.
In silico analyses of OmpA sequences. (A and B) Alignments of A. phagocytophilum OmpA with its homologs from A. marginale St. Maries strain (AM854), A. marginale subsp. centrale Israel strain (ACIS_00486), E. chaffeensis Arkansas strain (ECH_0462), Ehrlichia canis Jake strain (Ecaj_0563), and Ehrlichia ruminantium Welgevonden strain (Erum_5620) (A) and with O. tsutsugamushi Ikeda strain OmpA (OTT_1320) (B). The signal sequences of all proteins have been removed. The A. phagocytophilum OmpA amino acid numbers are listed above each set of aligned sequences. A. phagocytophilum OmpA amino acids that contain the cellular adhesion domain, determined as shown in Fig. 9, are denoted in boldface. Amino acids that are highly similar or weakly similar are underscored by two dots or one dot, respectively. (A) A. phagocytophilum OmpA amino acids that are predicted to be extracellular and to form a transmembrane domain are denoted by an asterisk and a plus sign, respectively, above them. Amino acids that are identical among all six, five of six, four of six, and three of six sequences are highlighted in red, yellow, green, and blue, respectively. If a given amino acid is identical among the three Anaplasma species sequences and the amino acid at the same position is identical among the three Ehrlichia species sequences but is different from the one in the Anaplasma species sequences, then the amino acid for only the Anaplasma species sequences is highlighted in blue. (B) Amino acids that are identical in the A. phagocytophilum and O. tsutsugamushi OmpA sequences are highlighted in red. (C) Predicted tertiary structure for A. phagocytophilum OmpA. The OmpA mature protein sequence was analyzed using the Phyre2 algorithm. The highest-scoring model (confidence value of 99.97%) that exhibited the greatest amino acid identity was for A. phagocytophilum OmpA amino acids 23 to 158 threaded on the crystal structure for amino acids 1 to 133 of Bacillus subtilis chorismate mutase, which is in the OmpA superfamily. The orange portion corresponds to amino acids 44 to 56, which is predicted to form a surface-exposed helix and loop. The red portions correspond to Lys 49, Tyr 51, Phe 52, Asp 53, and Lys 56 of the K[IV]YFDaXK peptide (where “a” is a nonpolar amino acid and “X” is any amino acid), which corresponds to A. phagocytophilum OmpA residues 49 to 56 and is conserved among Anaplasma spp., Ehrlichia spp., and O. tsutsugamushi OmpA proteins.