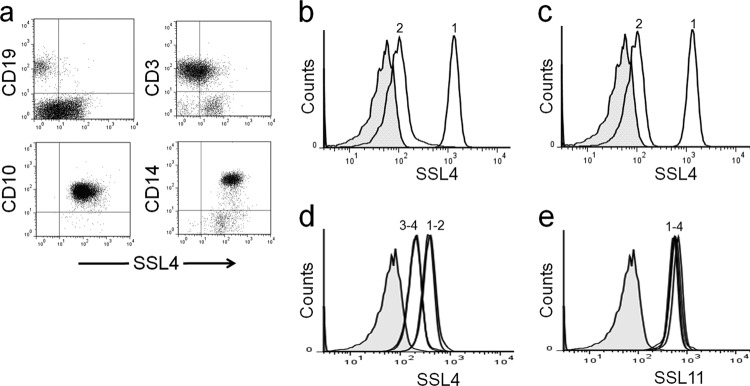
Fig 4.
Sialic-acid-dependent binding of SSL4t to human myeloid cells. (a) Human leukocytes double stained with rSSL4t-FITC (x axis) and PE-conjugated antibodies specific to monocytes (CD14), neutrophils (CD10), B lymphocytes (CD19), and T lymphocytes (CD3). (b) Binding of 0.1 μM SSL4t-FITC to human granulocytes untreated (peak 1) or pretreated (peak 2) with neuraminidase. (c) Human granulocytes stained with 0.1 μM SSL4t-FITC (peak 1) or 0.4 μM SSL4t-R182A-FITC (peak 2). (d) Human granulocytes stained with 0.01 μM SSL4t-488 (peak 1) plus 10-fold (0.1 μM) excess of either unlabeled SSL11 (peak 2), unlabeled SSL4t (peak 3), or unlabeled SSL4t-N181H (peak 4). (e) Human granulocytes stained with 0.01 μM SSL11-488 (peak 1) plus 10-fold (0.1 μM) excess of unlabeled SSL11 (peak 2), unlabeled SSL4t (peak 3), or unlabeled SSL4t-N181H (peak 4).