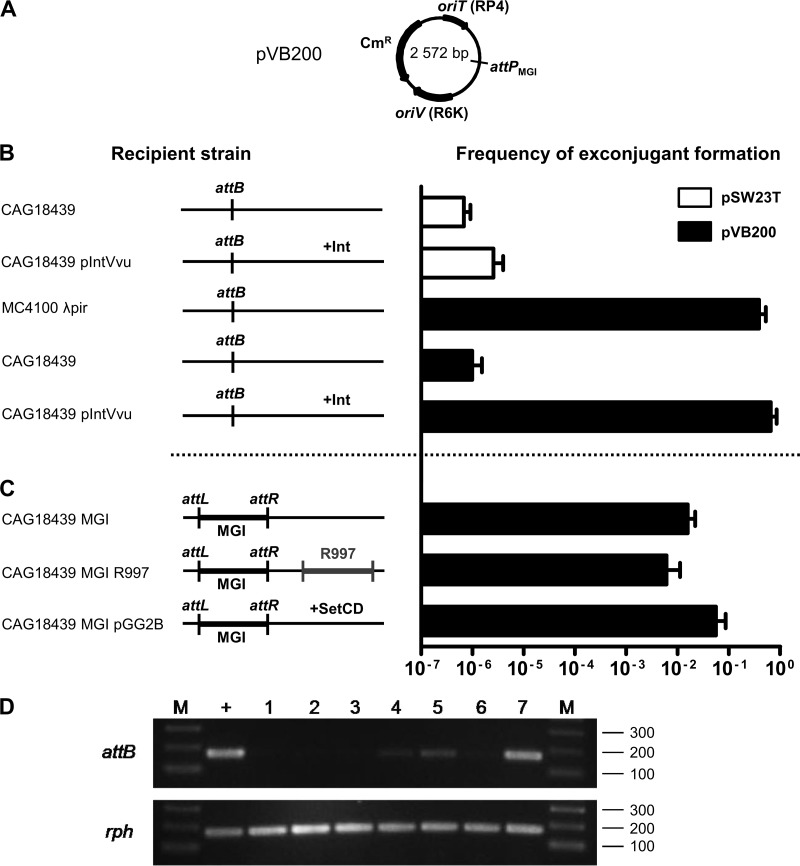
Fig 2.
Genetic requirements for integration and excision of a replication-deficient plasmid containing the attP site of MGIVflInd1. (A) Schematic map of pVB200. (B and C) Mobilization assays of pSW23T and pVB200 performed to assess plasmid integration into the 3′ end of yicC (attB). Conjugation assays were carried out using E. coli β2163 (pir+) as a donor and MC4100 λpir (pir+) or CAG18439 variants (pir) as recipient strains. The genetic background of each recipient strain is indicated on the left side of the panels. R997 is an Apr-conferring ICE of the SXT/R391 family. To induce expression of IntMGI from pIntVvu or of SetCD from pGG2B, the conjugation assays were carried out on media supplemented with 0.02% arabinose. The frequency of exconjugant formation was obtained by dividing the number of exconjugants (Tcr Cmr CFU for CAG18439 or Smr Cmr for MC4100 λpir) by the number of recipients (Tcr or Smr CFU, respectively). The bars indicate the mean values and standard deviations obtained from three independent experiments. (D) Analysis of excision of pVB200 integrated into yicC (attB). Ethidium bromide-stained 2% agarose gel of attB and rph fragments amplified by semiquantitative PCR. Lanes: M, 2-log molecular size marker; +, CAG18439; 1 and 2, CAG18439 yicC::pVB200 pIntVvu; 3, CAG18439 yicC::pVB200-MGIVflInd1; 4 and 5, CAG18439 yicC::pVB200-MGIVflInd1 prfC::R997; 6 and 7, CAG18439 yicC::pVB200-MGIVflInd1 pGG2B. Lanes 2 and 7, cultures were induced with 0.02% arabinose; lane 5, culture was induced with 100 ng/ml mitomycin C.