Fig 8.
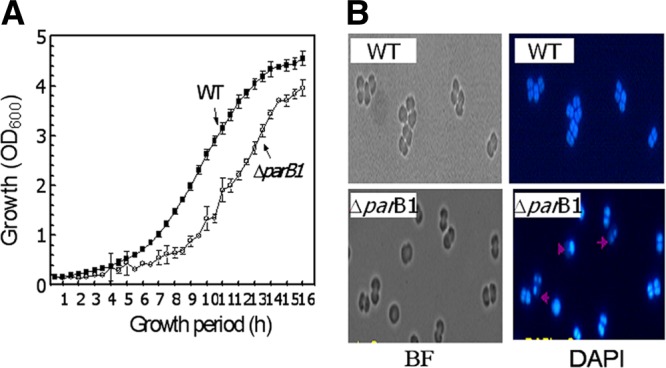
Effect of ParB1 deletion on genome maintenance in Deinococcus radiodurans. (A) The parB1 deletion mutant (ΔparB1) of D. radiodurans was generated, and its growth pattern at an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was compared with that of D. radiodurans R1 (wild type [WT]). (B) The effect of the parB1 deletion on anucleation was examined microscopically. Cells grown at different time intervals were micrographed under bright-field (BF) fluorescence, and cells were stained with DAPI. The percentage of anucleation was calculated from the number of cells missing a genome out of the total number of cells counted. Micrographs shown are those of wild-type and ΔparB1 mutant cells grown for 10 h under normal growth conditions.
