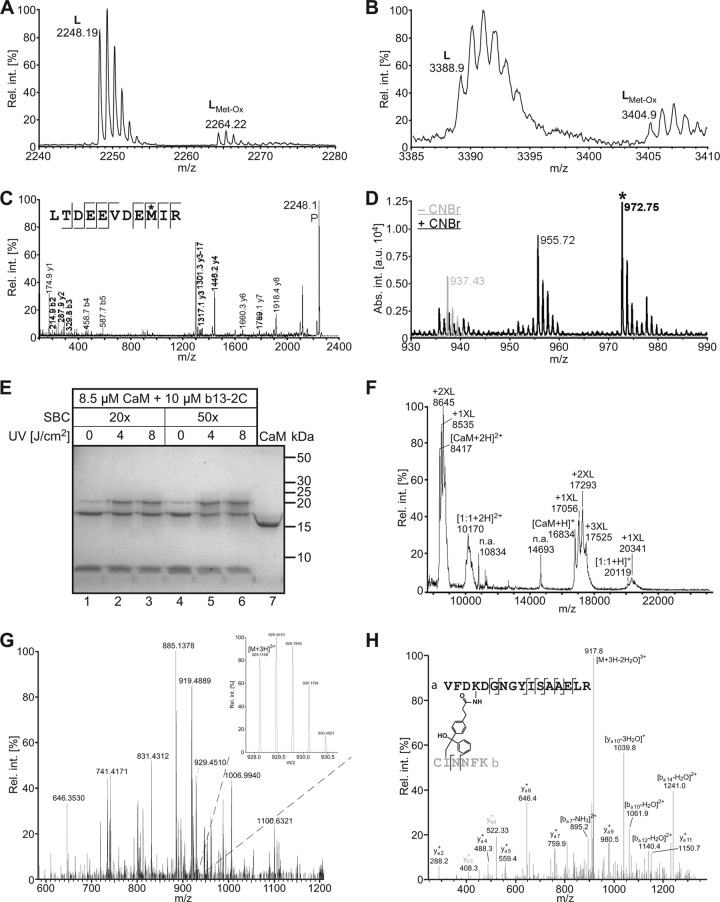
Fig 3.
Mapping of contact sites in bMunc13-2–CaM complexes. Covalent complexes of the Munc13 peptide b13-2C and CaM were generated either by PAL (A to D) or by chemical cross-linking with SBC (E to H), and the cross-linked sites were mapped by MS. (A and B) Detection of the cross-linked peptides Bpa723-b13-2C(1-6)–CaM(116-126) ([M + H]+calculated = 2,248.03 Da) (A) and Bpa723-b13-2C(1-6)–CaM(127-148) ([M + H]+calculated = 3,388.48 Da) (B) by LC-MALDI-MS. The signals with a mass increment of +16 mass units represent the same peptide with an oxidized Met. (C) Sequencing of Bpa723-b13-2C(1-6)–CaM(116-126) by MS. In the fragment ion mass spectrum, P denotes the precursor signal, and only b and y ions are labeled for the sake of clarity. On the basis of the conclusive N- and C-terminal ion series, Met-124 (asterisk) was identified as the site of photoincorporation into CaM. (D) CNBr cleavage of Bpa723-b13-2C(1-6)–CaM(127-148). The indicative signal at m/z 972.75 (asterisk) was absent before (−CNBr) but present after (+CNBr) cleavage and represents the methyl thiocyanate derivative of Bpa723-b13-2C(1-6) ([M + H]+calculated = 899.41 Da + 73.00 Da = 972.42 Da). Appearance of this signal upon CNBr cleavage clearly indicated photoincorporation into a Met side chain, most likely Met-144 rather than Met-145, as linkage through the former was somewhat more compatible with the fragment ion mass spectrum of Bpa723-b13-2C(1-6)–CaM(127-148) (not shown). The signal at m/z 955.72 (mass increment of −17 mass units) most likely represents the loss of ammonia by cyclization of the N-terminal S-carboxamidomethyl-Cys (19). (E) Coomassie-stained gel showing the influence of different conditions (excess of SBC, irradiation energy) on cross-linking yield. The faint bands corresponding to b13-2C–CaM complexes, which also appeared in the absence of UV light (lanes 1 and 4), are probably caused by a slight degree of photoreaction in ambient light. Control CaM in lane 7 was dissolved in water. (F) Detection of cross-linked b13-2C–CaM complexes by MALDI-TOF-MS. The mass spectrum shows the sample from lane 6 of the gel in panel E. Although the spectrum is dominated by signals for non-cross-linked CaM carrying up to three cross-linker molecules, the signals for 1:1 b13-2C–CaM adducts are clearly visible (m/z range of 20,000 to 21,000 for singly and 10,000 to 11,000 for doubly charged ions). (G) LC-MS/MS analysis of the cross-linked b13-2C–CaM complex after tryptic in-gel digestion. Although only of low abundance in the mass spectrum shown, the triply charged signal at m/z 929.1158 (see inset) identified the candidate cross-linked peptide b13-2C(1-6)–CaM(91-106) on the basis of its high mass accuracy ([M + H]+observed = 2,785.332 Da; [M + H]+calculated = 2,785.329 Da; mass deviation of 0.003 Da). (H) Sequencing of b13-2C(1-6)–CaM(91-106) by MS. The fragment ion mass spectrum confirmed the identity of the cross-linked peptide and revealed Lys-94 of CaM(91-106) to be linked to Ile-2 of b13-2C(1-6). Cross-linking at Cys-1 of b13-2C could not be excluded on the basis of the mass spectrometric data but was considered unlikely, as reaction to this site is unusual for benzophenones and would most likely lead to steric hindrance of tryptic cleavage. Rel. int., relative intensity in percent; abs. int., absolute intensity in arbitrary units.