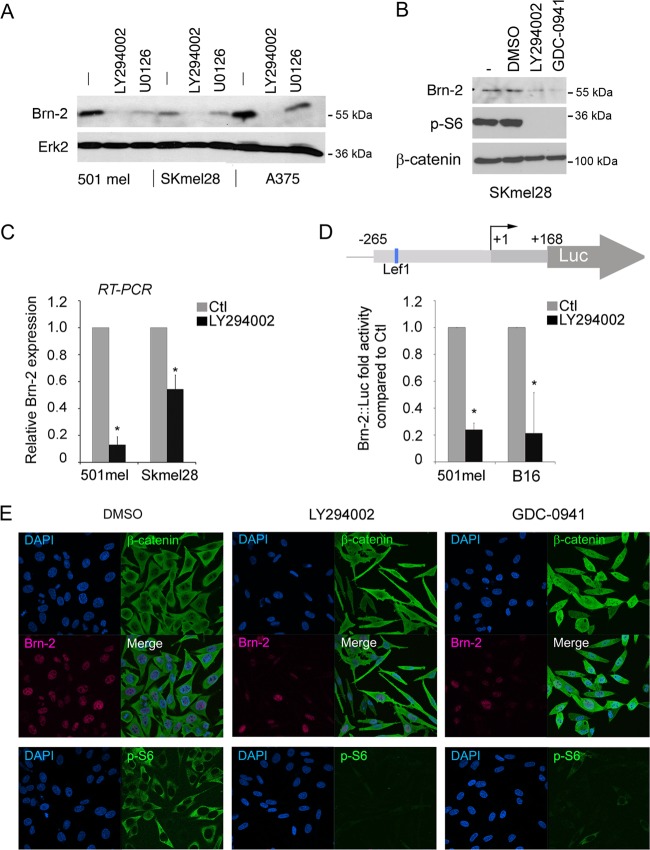
Fig 2.
PI3K inhibition decreases Brn-2 protein expression. (A) Western blot of 501mel, SKmel28, and A375 melanoma cells treated with LY294002 (25 μM) for 24 h. MEK inhibition (U0126; 10 μM) was used as a control, and Erk2 was used to ensure equal loading. (B) Western blot performed on SKmel28 cells treated with two different PI3K inhibitors (LY294002 at 25 μM or GDC-0941 at 10 μM) for 24 h using anti-Brn-2 and anti-p-S6 antibodies. β-Catenin was used as a loading control. (C) Relative expression of Brn-2 mRNA as determined using quantitative real-time RT-PCR from the indicated melanoma cell lines. Values were normalized to those for GAPDH and ratios were established compared to DMSO treatment. (D) Schematic of the Brn-2 promoter showing the binding site for Lef1 (top). Shown is a luciferase assay of 501mel and SKmel28 cells transfected with a Brn-2-luciferase reporter and treated with LY294002 or DMSO. Columns represent means from three experiments; bars indicate SD; *, P < 0.05. (E) PI3K inhibition does not affect β-catenin cellular localization. Immunofluorescence performed on SKmel28 treated with LY294002, GDC-0941, or DMSO (Ctl) using a monoclonal mouse anti-β-catenin (green), a polyclonal goat anti-Brn2, and a polyclonal rabbit anti-p-S6 antibody. Nuclei were counterstained using DAPI.