Fig 2.
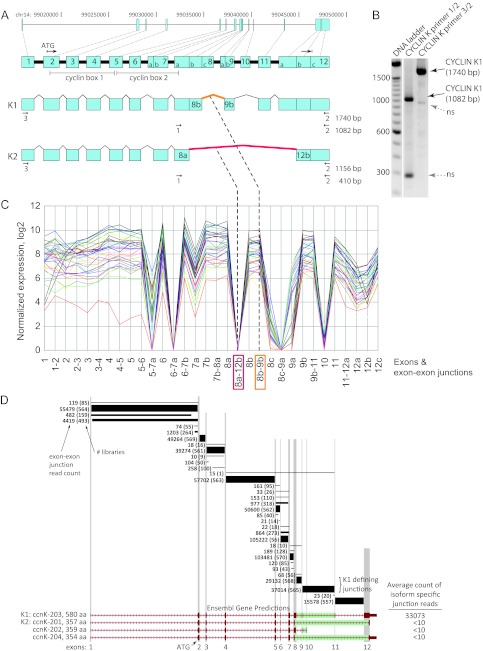
Cyclin K1 is the predominant cyclin K mRNA isoform. (A) Cyclin K gene exon arrangement and splicing. The exon arrangement of the CCNK locus on chromosome 14 is depicted. Splicing pathways that produce a 43-kDa isoform (cyclin K2) and a 64-kDa isoform (cyclin K1) are shown; subdivisions in exons 7, 8, 9, and 12 represent different known splice acceptors and donors observed in the mRNA and EST data. The numbered arrows depict primers and RT-PCR product sizes that were used to discriminate between the cyclin K1 and K2 isoforms. The 8b-9b (orange) and 8a-12b (red) exon-exon junctions differentiate the expression of the cyclin K1 and K2 isoforms, respectively. (B) Cyclin K1 mRNA is present in HeLa cells. RT-PCR of HeLa poly(A)-enriched RNA was performed with primer pairs 1/2 and 3/2 that were designed to differentiate between cDNAs for cyclin K1 and K2 (see panel A). RT-PCR products corresponding to the predicted size for cyclin K1 are indicated. Sequencing of the ∼300-bp and ∼950-bp bands showed that they are not cyclin K related, and they are denoted as nonspecific (ns). (C) RNA-Seq analysis of known cyclin K exons and exon junctions. The normalized expression of observed combinations of known splice donors and acceptor sites (Fig. 2A) for the CCNK locus for 38 human cancer and cell line mRNA libraries is shown. (D) Detection of cyclin K exon-exon junctions by HMMSplicer analysis of RNA-Seq data. Exon-exon junction RNA-Seq read counts (552,300 total) from 570 human cancer and cell mRNA libraries that mapped to the CCNK locus using HMMSplicer are shown. The junctions putatively connect the exons (vertical gray bars) for the Ensembl-predicted gene transcripts (red, bottom). Total read count among the 570 libraries for each junction read is shown; in parentheses is the number of libraries where the junction read was observed. The thickness of each line approximates the relative abundance of the junctions. In the exon 8 region, three different splice donor sites (Fig. 2A) are used between four Ensembl transcripts. The green bars represent the junctions or junction combinations that would uniquely define each of the Ensembl-predicted isoforms. The number of counts observed for each of the isoform-defining junctions is shown in the right-hand column. For the K1 isoform (CCNK-203), the isoform-specific read count, 33,073, is the mean of the counts of the two K1-defining junctions (29,132 and 37,014).