Fig 2.
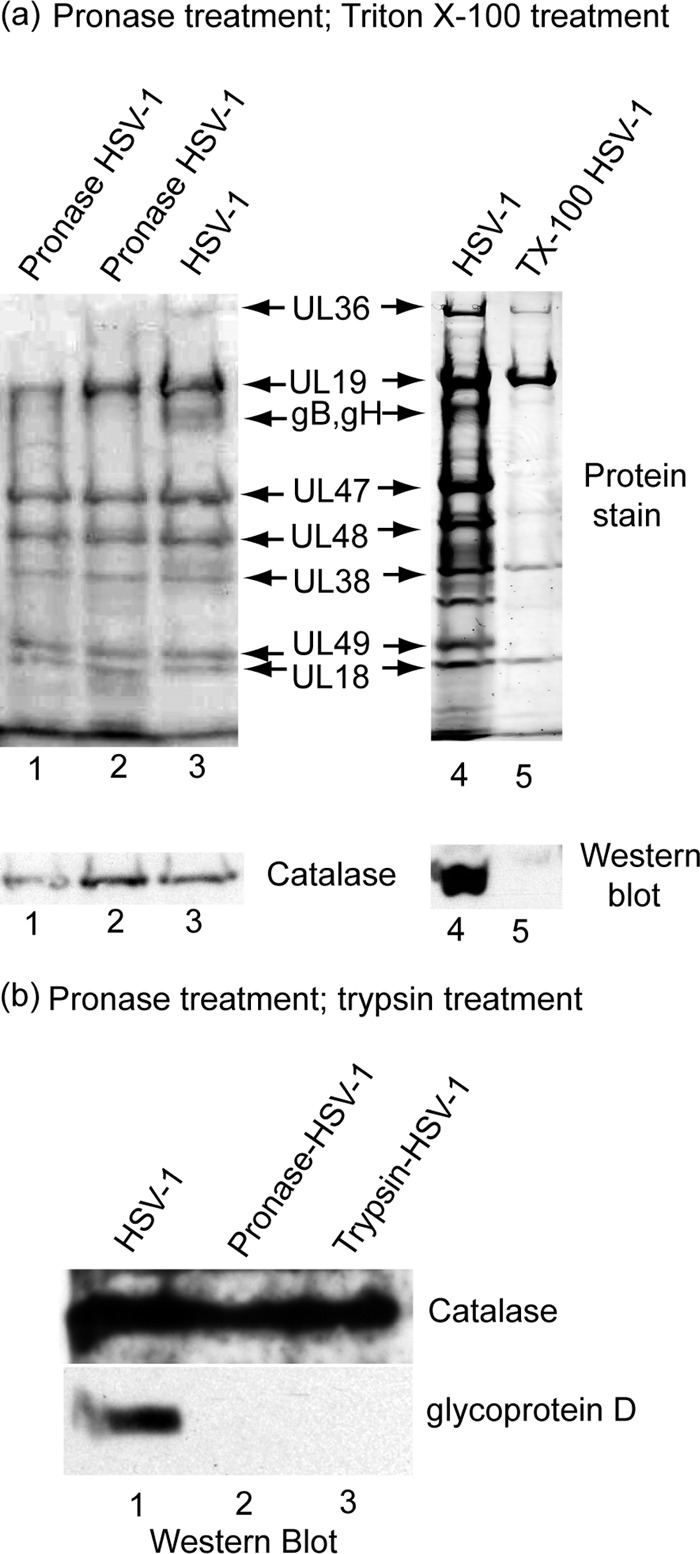
Localization of catalase in HSV-1 by treatment of purified virions with pronase (lanes 1 to 3) and Triton X-100 (a, lanes 4 and 5) and by pronase and trypsin treatment (b, lanes 1 to 3). Panel a shows SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis of proteins present in intact HSV-1 (lanes 3 and 4) and in virions after treatment with pronase (lanes 1 and 2) and Triton X-100 (lane 5). Note that catalase was found to be present in intact virions (lanes 3 and 4) and in pronase-treated virions (lanes 1 and 2) but not in virions after treatment with 1% Triton X-100 (lane 5). Pronase treatment was carried out by digesting purified HSV-1 (0.25 mg/ml) with 1 mg/ml pronase (Streptomyces griseus; Calbiochem 537088) for 4 h at 37°C. After pronase treatment, the virus was reisolated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation prior to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. Triton X-100 treatment was performed by adjusting purified virus to 1% Triton X-100 in TNE buffer containing 10 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) and incubating for 15 min on ice (4°C). The resulting capsids were then purified by sucrose gradient centrifugation before SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. (b) Western blot analysis of purified HSV-1 after treatment in vitro with pronase or trypsin. A total of 100 μl of purified HSV-1 (1 mg/ml) was adjusted to 2 mg/ml pronase or 2 mg/ml trypsin. A control incubation had no enzyme. Mixtures were incubated for 2 h at 37°C, and virions were purified away from enzymes by centrifugation on a 20% to 50% sucrose gradient as described in the legend to Fig. 1. Virus specimens were pelleted by centrifugation and examined by SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. Blots were stained for catalase (rabbit polyclonal; see above) and glycoprotein D (mouse monoclonal antibody DL11; a gift from Gary Cohen and Roselyn Eisenberg; 1:5,000). Note that protease treatment caused digestion of glycoprotein D, but not catalase, indicating that catalase is located inside the HSV-1 membrane.
