Fig 6.
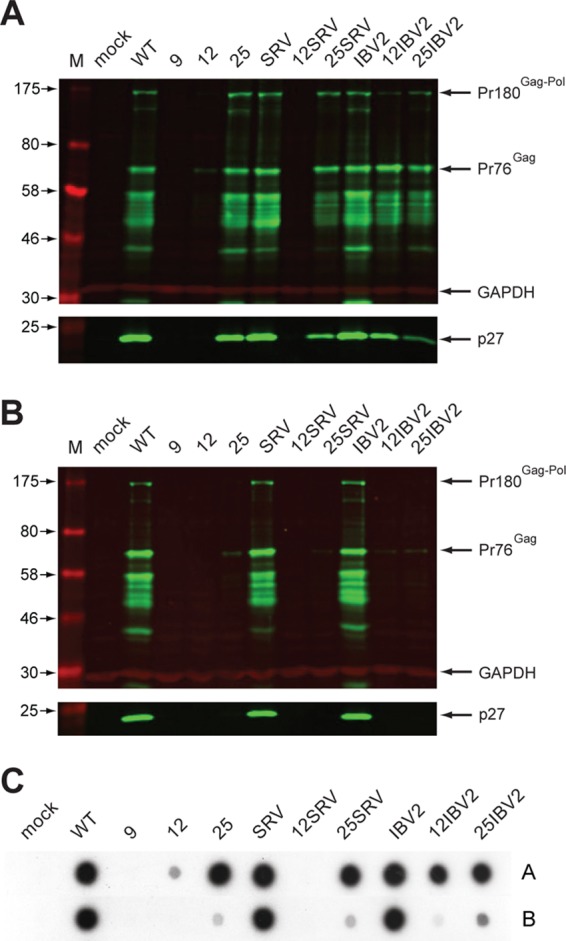
Multipassage infectivity assay. (A, B) DF1 cells were transfected with pRCAS-WT or mutant derivatives, and released virus was used subsequently to infect new cells as detailed in Materials and Methods. Three sequential rounds of infection were carried out. In round 1, two different volumes (500 μl or 50 μl, corresponding to a 1:10 or 1:100 dilution, respectively) of medium from transfected cells were used to infect two new dishes of cells. Three days later, the procedure was repeated, generating four dishes in infection round 2, and the process was repeated again, generating eight infected-cell dishes in round 3 (dishes 3.1 to 3.8). Cell lysates (upper panel) and supernatant virus (lower panel) from the eight dishes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (8% and 15% gels, respectively) and Western blotting using a polyclonal anti-CA (p27) serum. Molecular sizes (in kDa) are indicated on the left. Shown in panel A is the Western blot from dish 3.1, infected with medium that had received the larger volume of medium at each round of the infectivity assay (500 μl for each of the three rounds), and in panel B, that from dish 3.8, which received the lowest (50 μl for each of the three rounds). GAPDH was used as a loading control. All viral proteins were detected with a green fluorescent secondary antibody, and GAPDH with a red fluorescent secondary antibody. (C) Reverse transcriptase activities of supernatant virus harvested from dishes 3.1 (row A) and 3.8 (row B). Virus particles were harvested from 1 ml culture medium by ultracentrifugation, and reverse transcriptase activity was assayed. Incorporation of [α-32P]dTTP was visualized by autoradiography.
