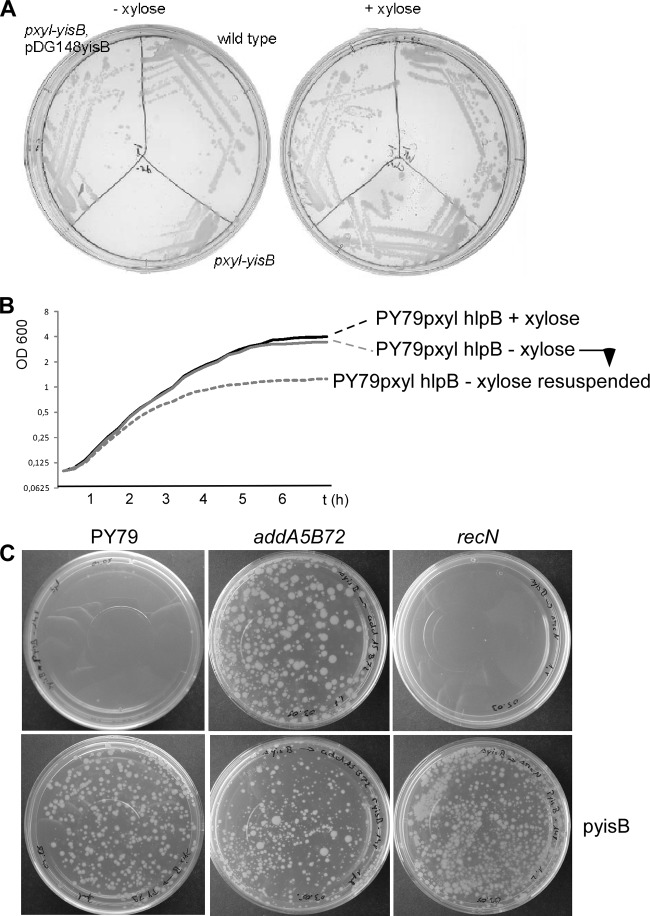
Fig 1.
(A) Growth of Bacillus subtilis strains in the presence or absence of inducer (xylose) driving synthesis of HlpB. pxyl-hlpB, transcription of hlpB (encoding HlpB) depends on presence of xylose; pDGhlpB, plasmid expressing hlpB; wild type, JM11 (scpA-yfp) strain expressing a functional YFP fusion unrelated to HlpB that grows on plates containing chloramphenicol. (B) Growth curves of B. subtilis strain VK01 (pxyl-hlpB) in minimal medium (plus Casamino Acids) in the presence (black line) or absence (gray line) of xylose. Dashed gray line, cells grown in the absence of xylose resuspended into fresh medium lacking xylose. (C) Competent cells transformed with 0.01 μg of chromosomal DNA from MH44 (hlpB::tet, pDGhlpB), selecting for tet resistance. Note that all strains could be transformed by an unrelated marker (comEA::cat).