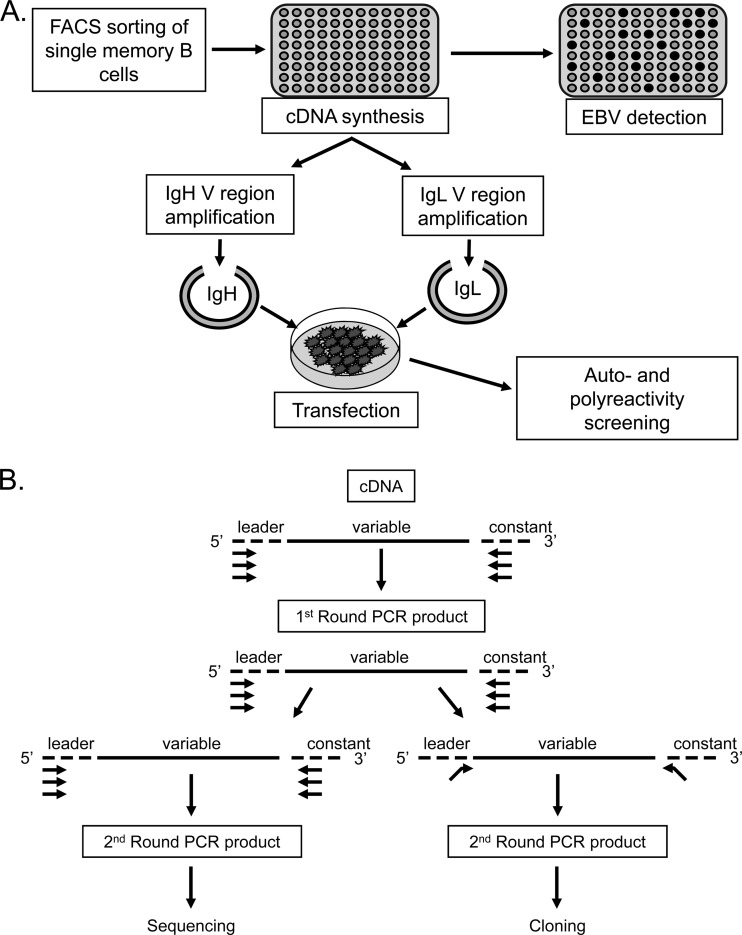
Fig 1.
Schematic representation of the cloning and expression methods used in this study. (A) Single CD19+ IgD− memory cells were sorted into 96-well plates, and cDNA was prepared. A fraction of this cDNA was then used to distinguish EBV+ from EBV− cells on the basis of the detection of the abundant EBV small RNA EBER1. The remaining cDNA was used for PCR amplification of Ig heavy- and light-chain variable regions (see below), which were cloned into expression vectors and transfected into 293T cells essentially as described by Tiller et al. (33). The resulting secreted antibodies were then purified and used for self- and polyreactivity assays. (B) PCR amplification of heavy- and light-chain variable regions (adapted from references 33 and 39). The first round of PCR used multiplex primers. A second round of amplification was performed in order to acquire sufficient PCR product for sequencing and identification of the individual V(D)J genes composing the VH and VL regions of a given cell. This round used separate reactions to amplify VH and VL PCR products. Sequences were aligned with the closest germ line sequences using the IMGT/V-QUEST database (http://www.imgt.org/IMGT_vquest/share/textes/). In parallel, PCR was also performed using the first-round products as a template and primers with restriction sites to allow subsequent cloning into expression vectors according to the protocol of Tiller et al. (33).