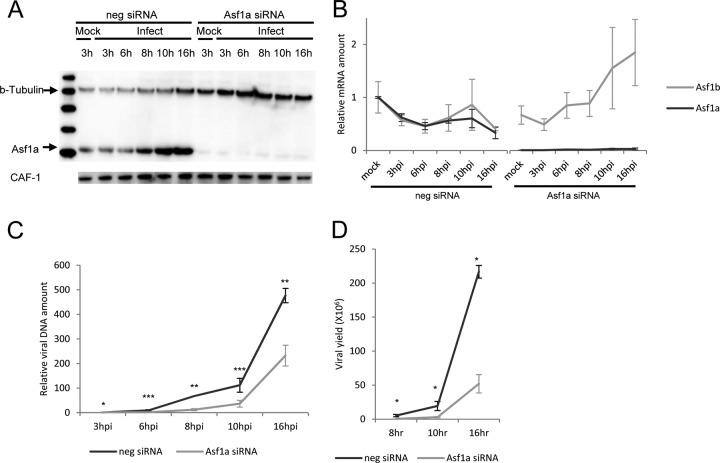
Fig 1.
Effect of Asf1a knockdown on HSV-1 growth. HeLa cells were transfected with Asf1a siRNA for 2 days, infected with HSV, and harvested at the indicated time p.i. (A) Asf1a siRNA knocks down Asf1a protein levels. Cells were lysed and immunoblotted with rabbit anti-Asf1a or β-tubulin or CAF-1 antibody. The reduction in the Asf1a protein is 93%. Interestingly, HSV infection induces Asf1a expression. (B) Asf1a siRNA specifically knocks down Asf1a mRNA, not Asf1b. Total mRNA was isolated and reverse transcribed. Asf1a and Asf1b mRNA levels (relative to a mock-infected sample) were determined at various times p.i. by qPCR and normalized to 18S rRNA levels. (C) Asf1a siRNA delayed viral DNA replication. Accumulated viral DNA was quantified by qPCR with TK promoter primers and normalized to GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) levels. The relative viral DNA amount was calculated based on a 3-hpi sample in negative (neg) siRNA-treated cells. (D) Asf1a siRNA delayed virus replication. Viral yield from Asf1a knockdown cells was significantly reduced at 8 hpi (18-fold), 10 hpi (7-fold), and 16 hpi (4-fold). Viral yields were determined by a plaque assay as described in Materials and Methods. All data are the averages of three independent experiments, and error bars represent the standard deviation. Student t test values are displayed with asterisks (*, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001).