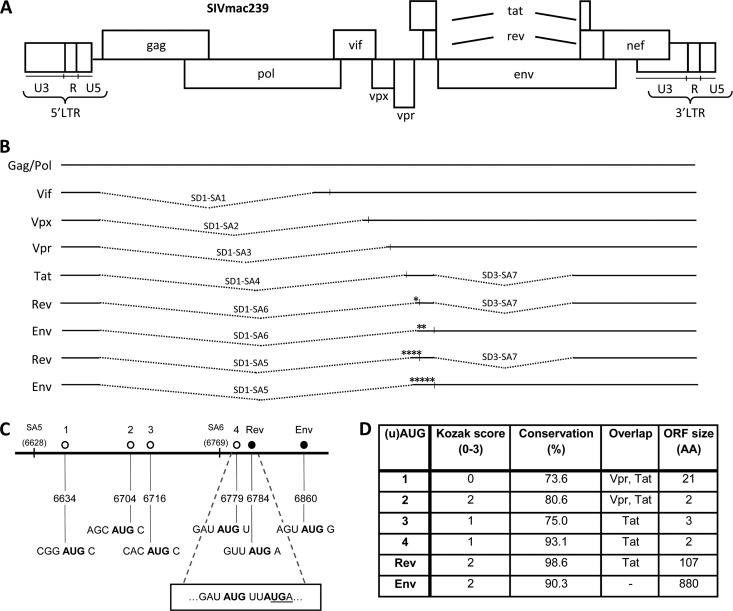
Fig 1.
SIV displays a complex splicing pattern, and upstream AUGs are present in the Rev and Env mRNAs. (A) The SIV DNA genome. (B) SIV mRNA splice variants with the encoded protein indicated on the left. The splice donor (SD) and splice acceptor (SA) sites used in SIV mRNA are indicated, along with the regular AUG start codons (vertical lines) and the upstream AUGs (*). (C) Start codons present between SA5 and the Env start codon in the SIV RNA genome. The uAUGs are depicted by an open circle, and the regular AUGs for Rev and Env by a filled circle with the name on top. The positions of SA5 and SA6 are marked. Below are the genomic positions and the sequence surrounding each AUG for comparison to the Kozak consensus sequence. The overlap between the uORF starting at uAUG4 and the Rev AUG is shown in a box with AUGs in bold and the uORF4 stop codon underlined. (D) Characteristics of each uAUG. Kozak score: a score was awarded based on the match with the Kozak consensus sequence (RCCAUGG) at positions −3 (A or G), −1 (C), and +4 (G), yielding a total score from 0 to 3. Conservation is the percentage of SIV isolates with the respective AUG based on all (n = 72) SIV sequences in the HIV Sequence Compendium 2011 (36). Overlap lists the viral ORFs with which each uAUG-ORF overlaps. ORF size is the length of the ORF served by each uAUG, indicated by the number of encoded amino acids (AA).