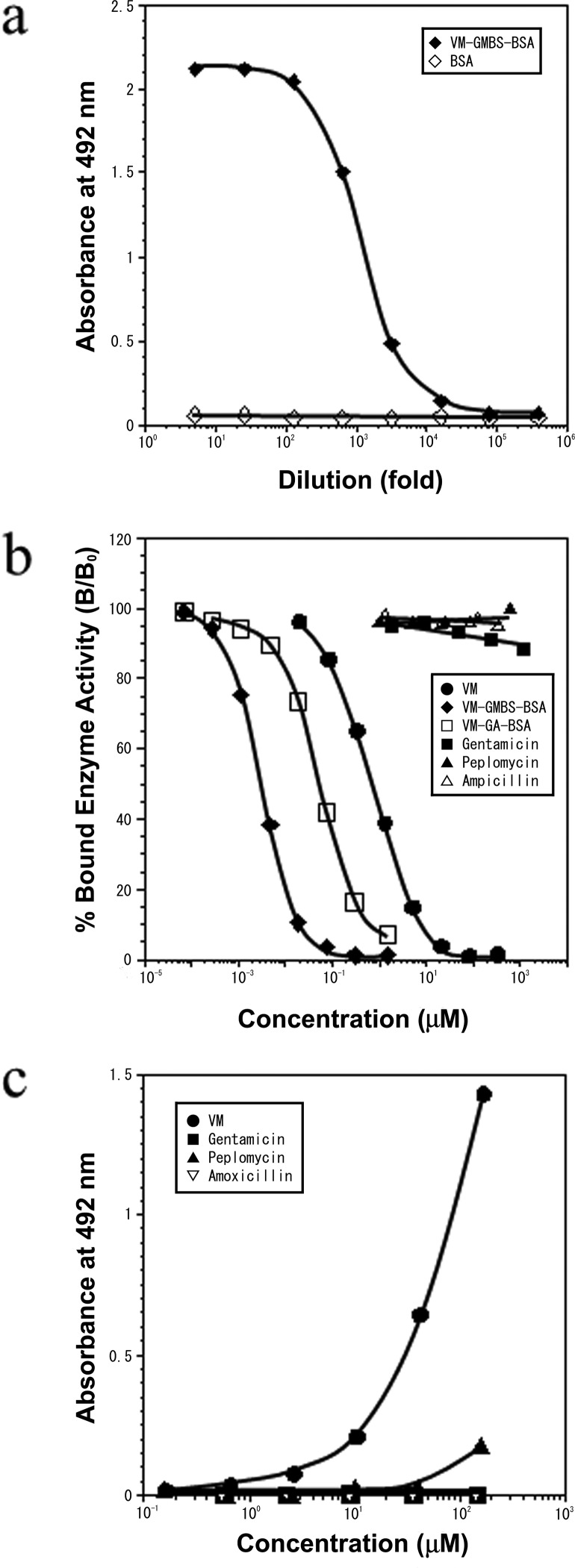
Fig 1.
(a) ELISA measurements of the binding of serially diluted anti-VM MAb (AVM-113) to the solid phase coated with VM-GMBS-BSA or BSA. (b) Reactivity of the AVM-113 MAb as measured by its immunoreactivity in the inhibition ELISA. The curves show the amount (percentage) of bound enzyme activity (B) for various doses of VM-GMBS-BSA, VM-GA-BSA, or free VM as a ratio to that bound using the HRP-labeled second antibody alone (B0). The concentration of VM in the conjugate VM-GMBS-BSA or VM-GA-BSA was photometrically calculated, assuming the molar extinction coefficient of BSA to be 43,000 at 280 nm and the other part (VM-GMBS or VM-GA) of each the conjugates to be ignored. (c) Reactivity of the AVM-113 MAb as determined from its immunoreactivity in the binding ELISA. Activated wells prepared for the binding ELISA were incubated with various concentrations of VM, GM, peplomycin, or AMPC. The wells were reacted with NaBH4 and then with HRP-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (whole; 1:2,000).